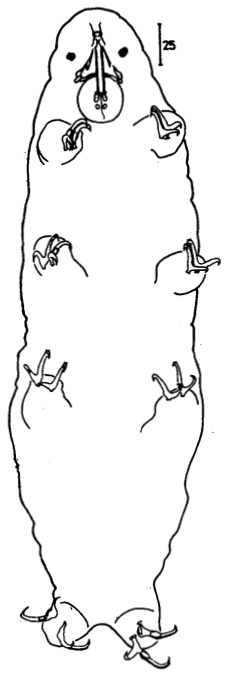
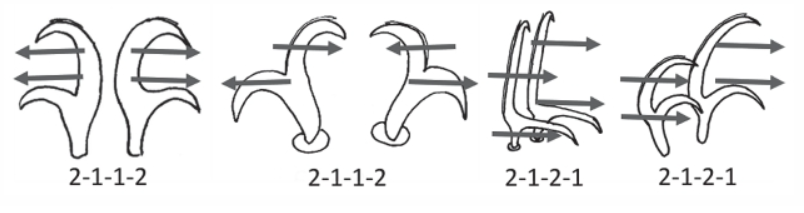
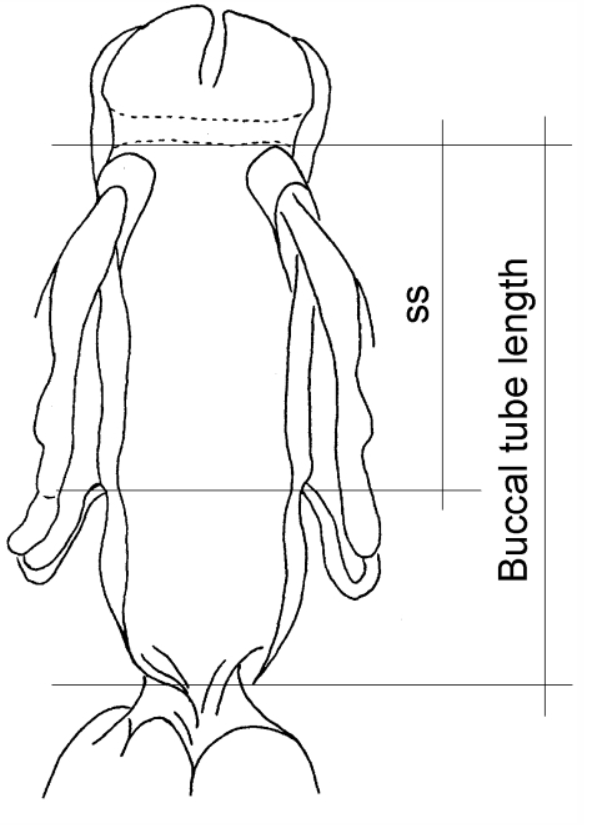
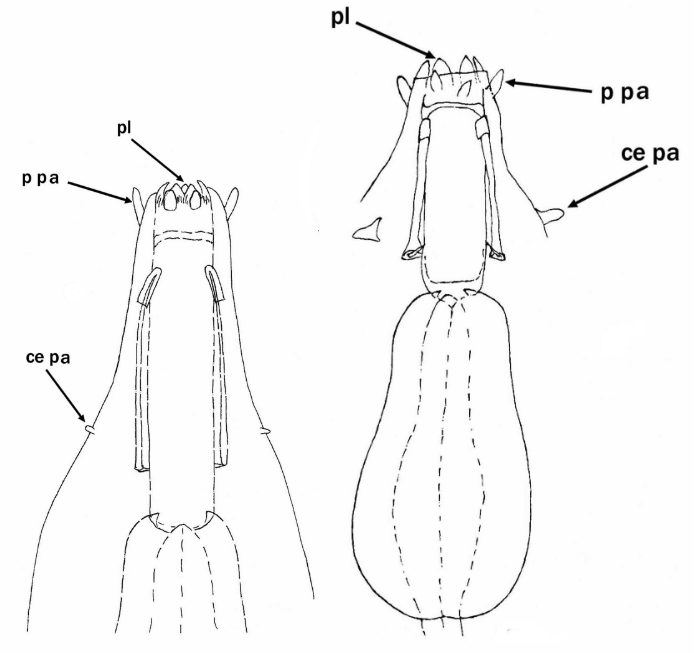
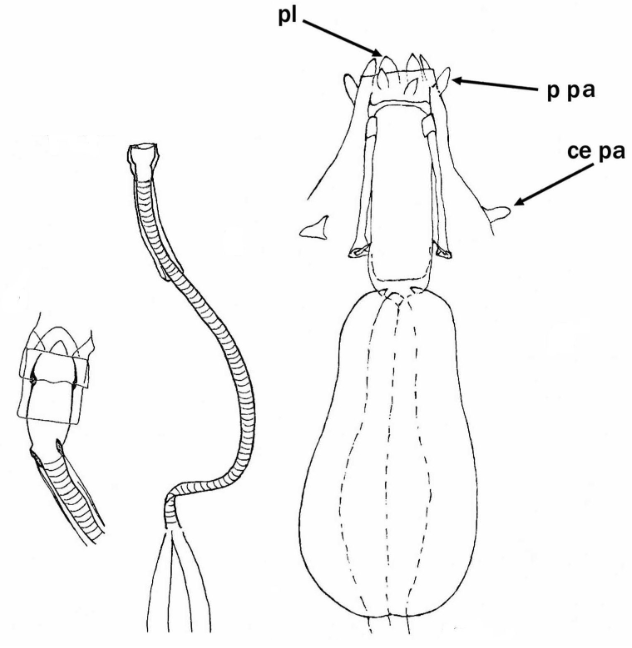
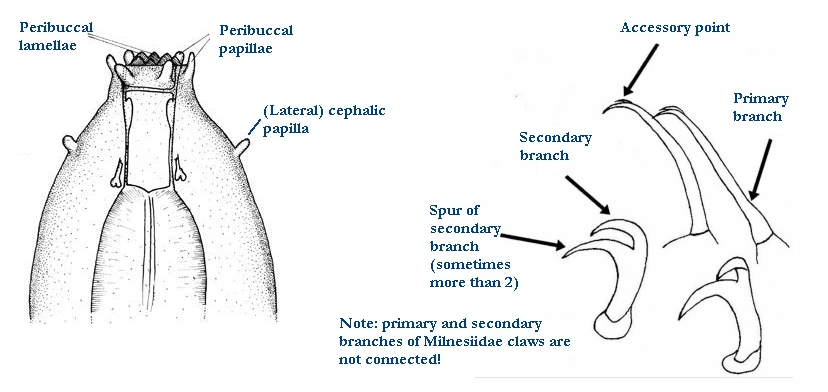
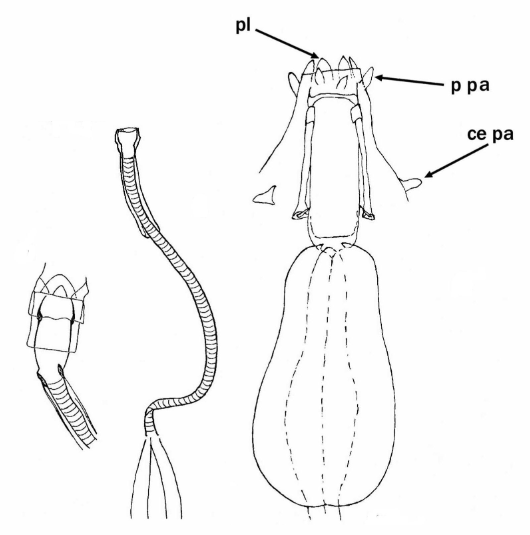
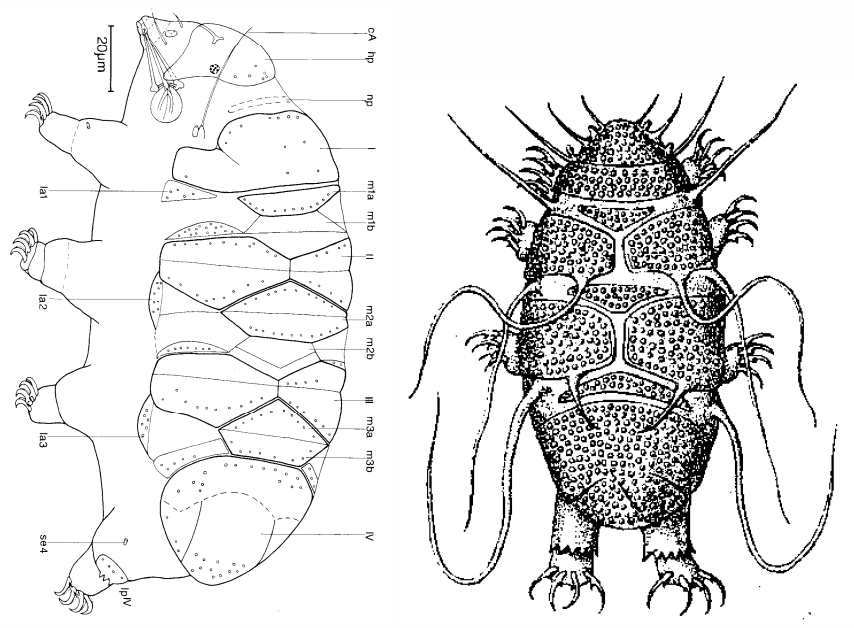
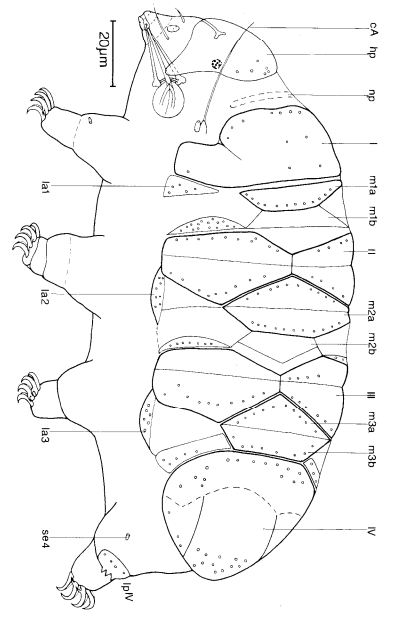
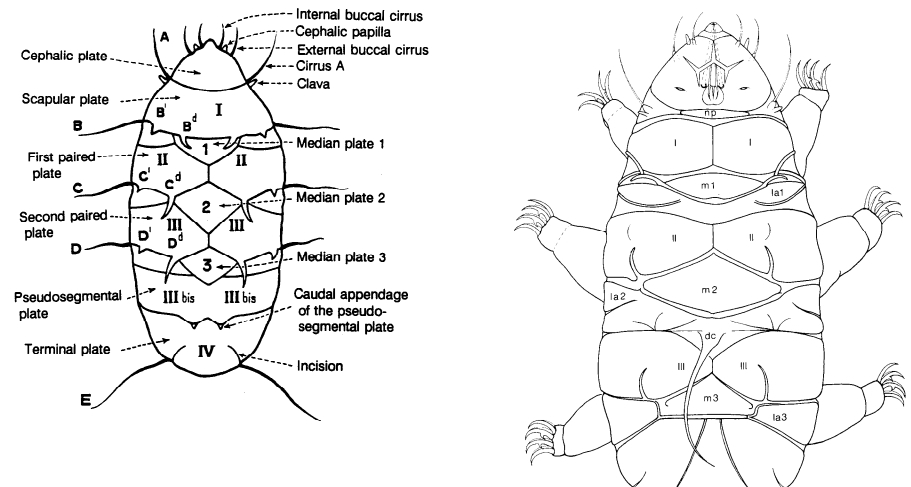
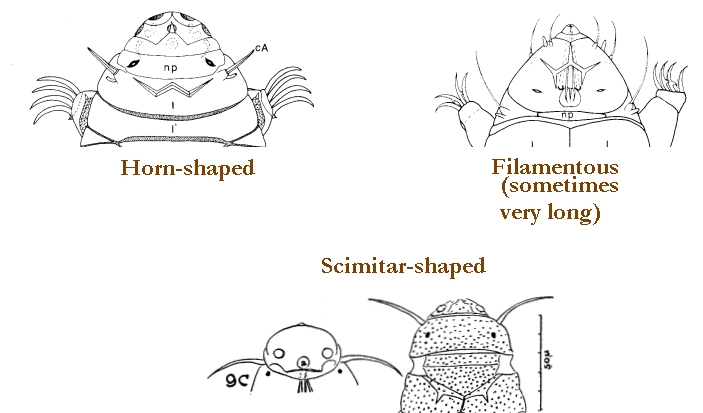
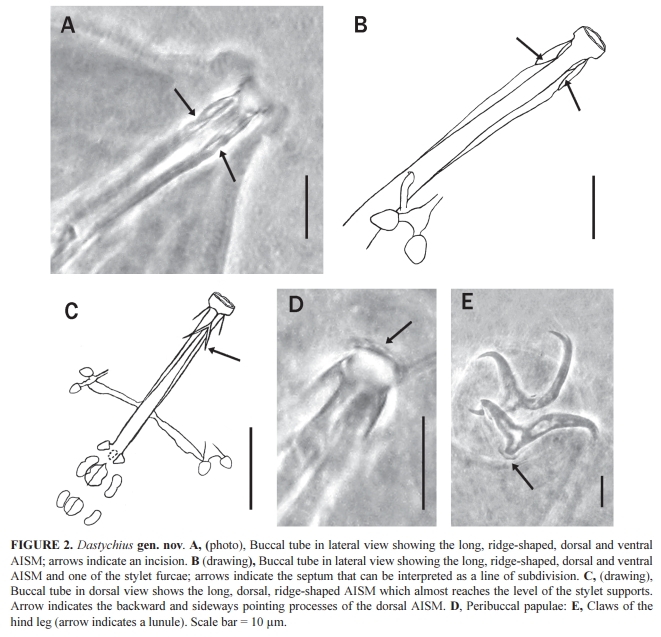
Genus description from Pilato 2013: “Claws of the Isohypsibius type; double claws of the same leg slightly different in shape and size; rigid buccal tube without ventral lamina but with a dorsal and a ventral apophysis for the insertion of the stylet muscles in shape of long, continuous ridges tailing off caudally and almost reaching the level of the stylet supports; anterior portion of both apophyses with caudal processes pointing backwards and sideways. At about a quarter the length of the ridged apophyses is an incision and septum. Six peribuccal lobes present; peribuccal lamellae absent; structures in the form of peribuccal papulae present, but this should be confirmed. Stylet furcae typically shaped, i.e. the basal portion of the two caudal branches are enlarged with thickened, swollen, and rounded apices; pharyngeal bulb with apophyses and placoids. Lunules present in the monotypic species. Smooth eggs laid in the exuvium.”
Citations:
Pilato G. 2013. The taxonomic value of the structures for the insertion of the stylet muscles in the Eutardigrada, and description of a new genus. Zootaxa. 3721 (4): 365-378.