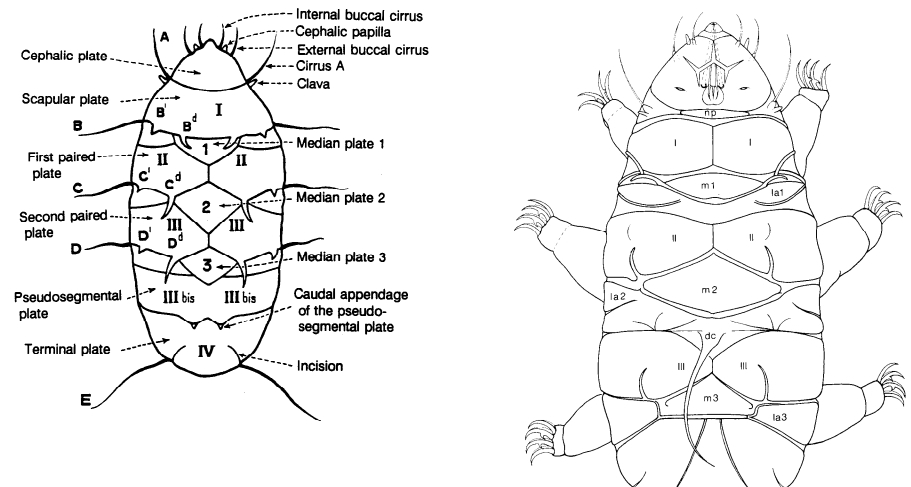
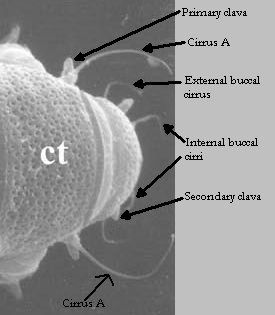
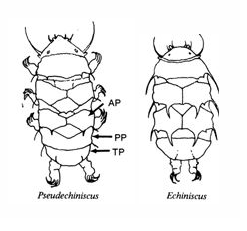
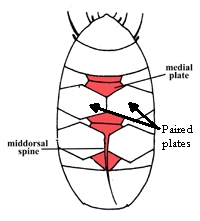
Eohypsibioidea

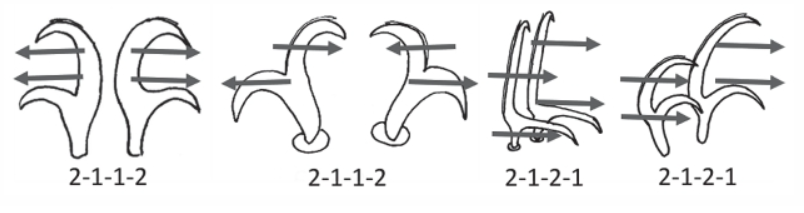
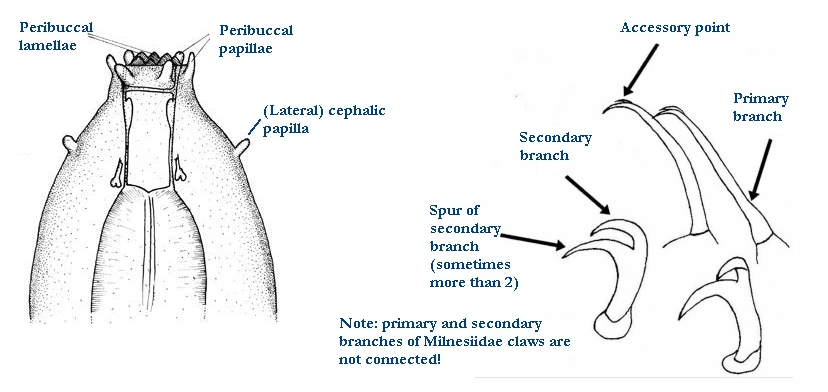
{Double claws similar in shape and arranged asymmetrically with respect to themedian plane of the leg (conventionally described as sequence 2121); claws may beof similar size; double claws of Eohypsibiidae type (¼Bertolanius type): subdividedinto three distinct sections, basal section, secondary branch and primary branch(rigidly joined to the secondary branch), one on top of the other […]
Eohypsibiidae

Eohypsibiidae from Marley et al. 2011: Eohypsibiidae-type claws, which are clearly delineated by septa, in linear order, from basal section, secondary branch and primary branch. The angle between basal section, secondary branch and primary branches are different between claws on the same leg and the internal claw can rotate on its base by 180°. Need description here […]
Bertolanius

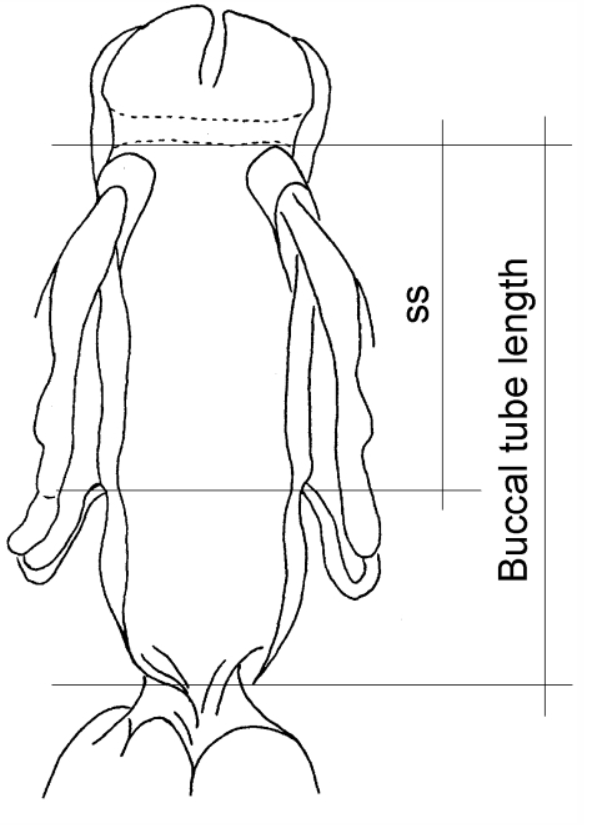
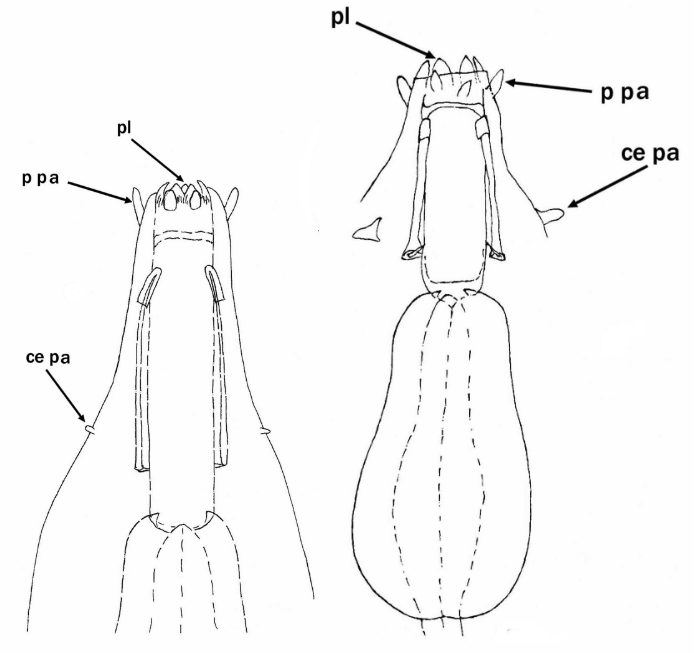
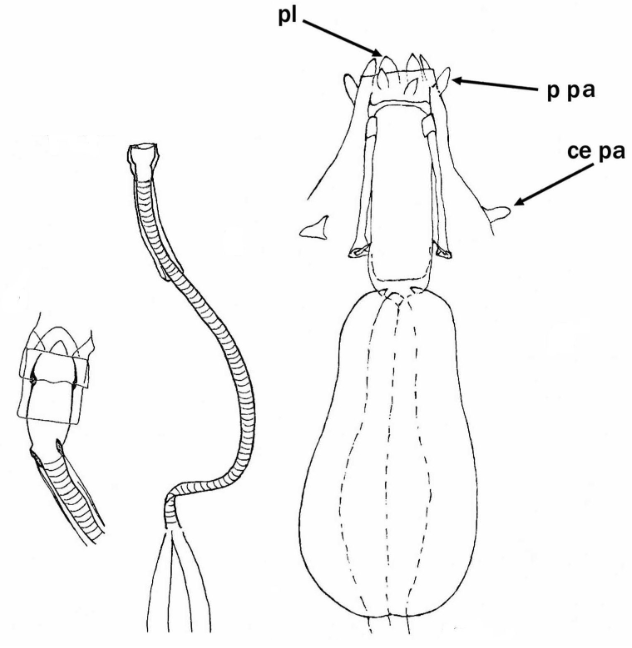
Genus description from Bertolani 1981: “Amphibolus-type claws (that is asymmetric claws, each constituted of three clearly defined sections one on top of the other), crest-shaped appendices for the insertion of stylet muscles on the buccal tube, buccal lamellae curving inwards, and freely laid ornamented eggs.” Citations: Bertolani R. 1981. The taxonomic position of some eutardigrades. […]
Austeruseus
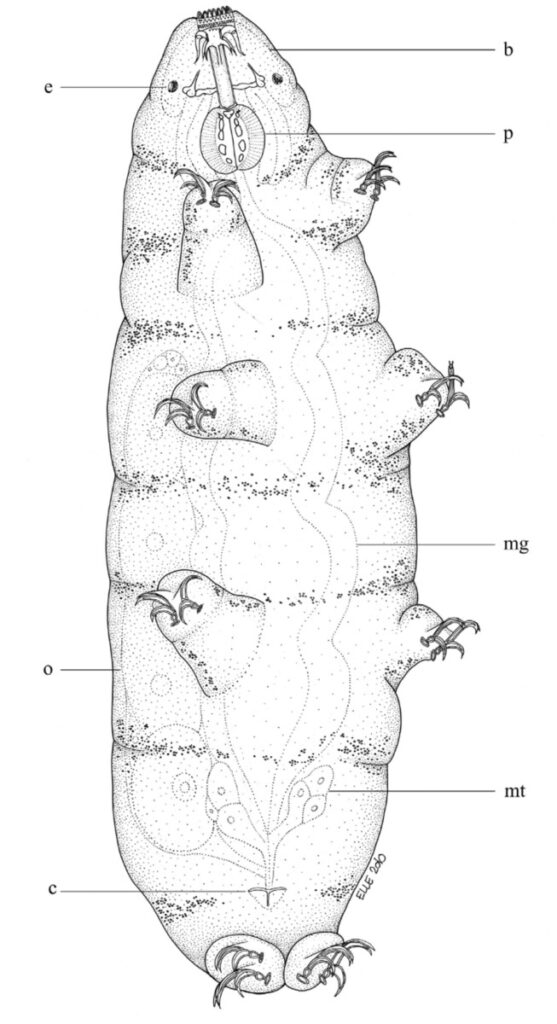
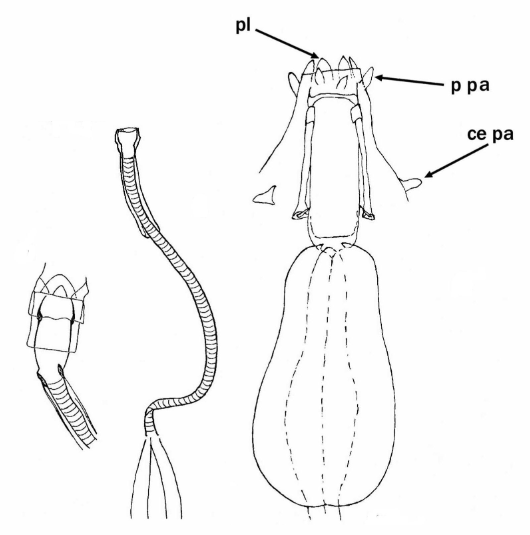
Austeruseus from Trygvadóttir & Kristensen 2011 in Degma & Guidetti 2018: “Rigid straight buccal tube; 2 to 6 hook-shaped appendages for insertion of the stylet muscles present on the sides of the buccal tube; the mouth tubular; ventral cuticular enforcement of the buccal tube as a thin line (instead of ventral lamina). Eggs laid freely.” […]
Eohypsibius
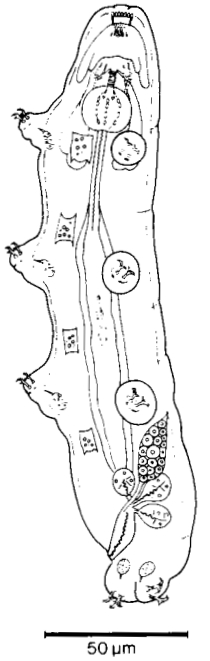
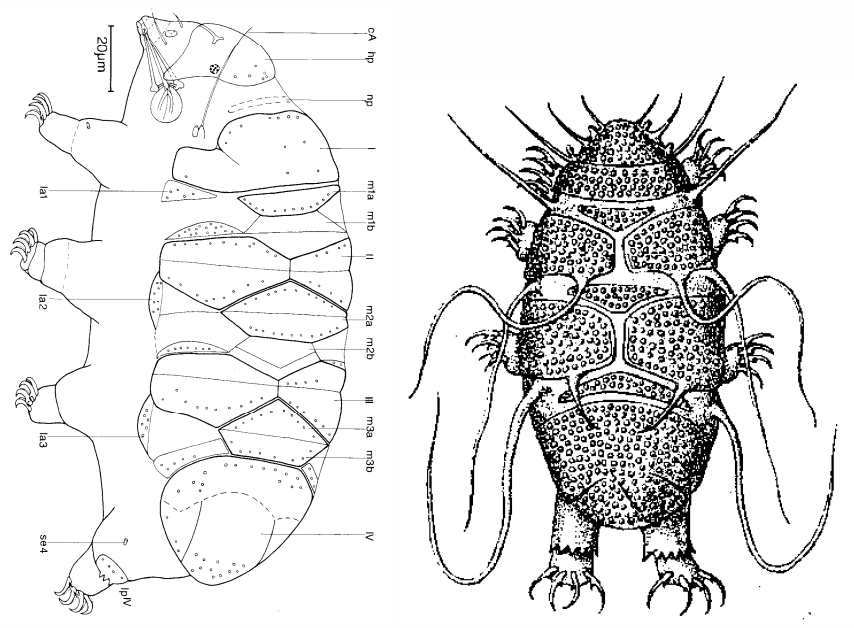
Genus description from Kristensen 1982: “An extremely slender calohypsibid with reduced legs and claws. Mouth opening large with 14-16 lamellae. A complete set of teeth in the buccal lumen; annulated buccal tube. Apophyses ventrally and dorsally hook-shaped and attached to the stylet retractor muscles. Claws of the Calohypsibius-type, but with lunules. Malpighian tubules ovoid with […]