Tardigrade Key
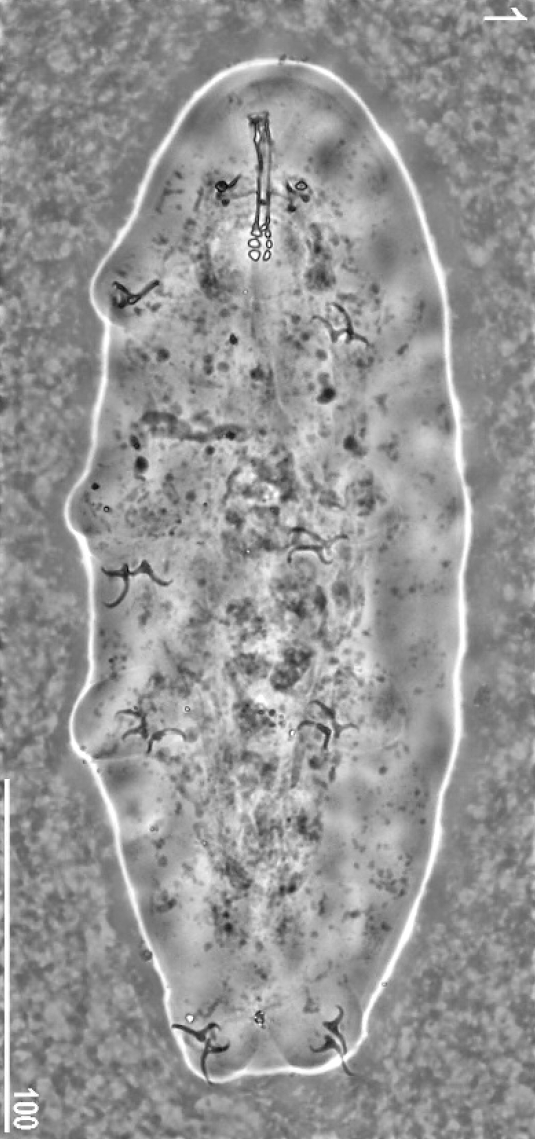
Doryphoribius
Isohypsibioidea from Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela. Claws asymmetrical (2121); Isohypsibius-type claw pairs;

Isohypsibioidea from Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela. Claws asymmetrical (2121); Isohypsibius-type claw pairs;
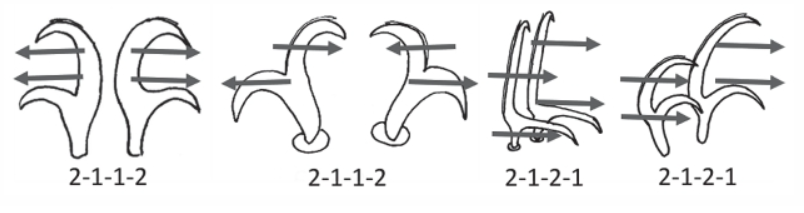
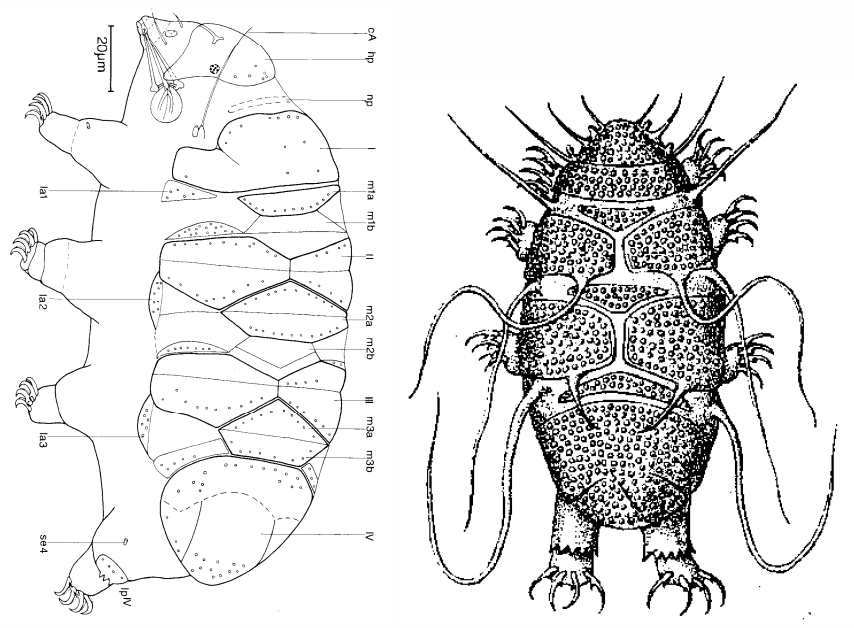
Image from Bingemer J, Hohberg K. 2017. An illustrated identification key to the eutardigrade species (Tardigrada, Eutardigrada) presently known from European soils. Soil Organisms. 89 (3): 127-149.
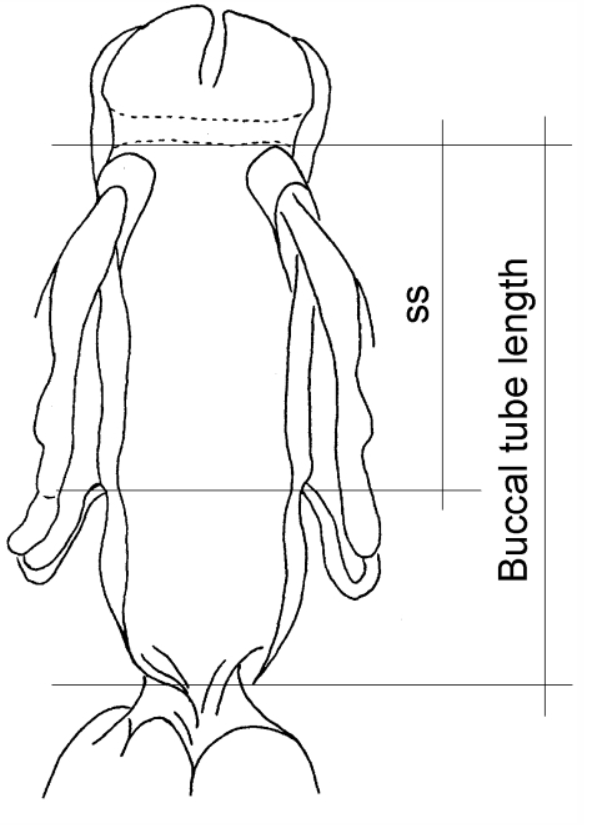
Stylet support insertion point = ss divided by Buccal tube length, as %. Note anterior measurements begin at anterior margin of stylet sheaths, ss is centred where stylet supports reach buccal tube (this requires a good dorsal or lateral view for proper measurement)
Image from Tumanov DV. 2006. Five new species of the genus Milnesium (Tardigrada, Eutardigrada, Milnesiidae). Zootaxa. 1122: 1-23.
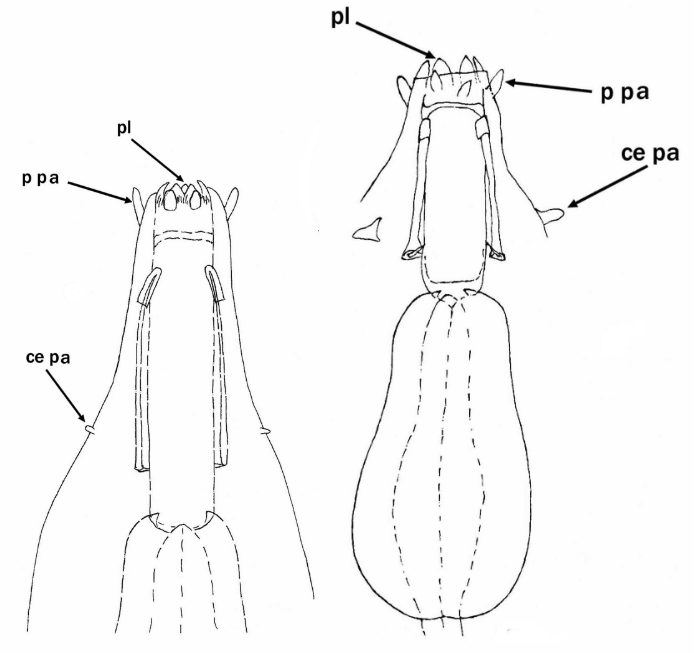
Images from Pilato G, Binda MG. 2010. Definition of families, subfamilies, genera, and subgenera of the Eutardigrada, and keys to their identification. Zootaxa. 2404: 1-54.
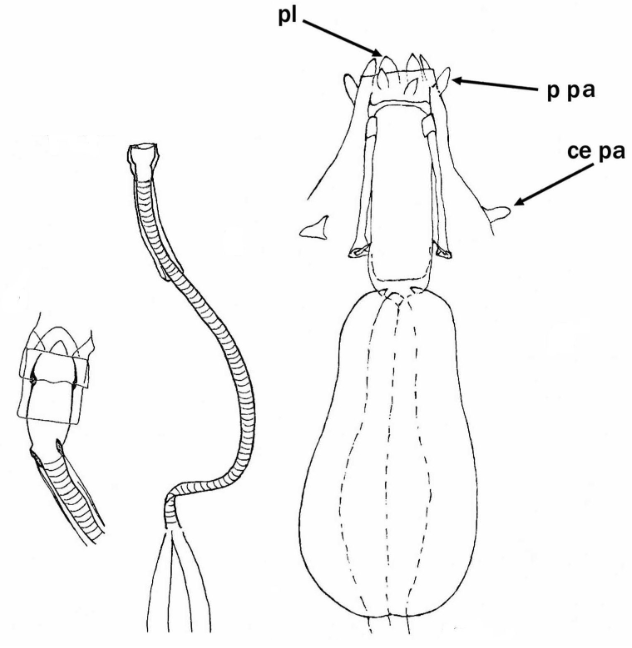
Images from Pilato G, Binda MG. 2010. Definition of families, subfamilies, genera, and subgenera of the Eutardigrada, and keys to their identification. Zootaxa. 2404: 1-54.
Images from Pilato G, Binda MG. 2010. Definition of families, subfamilies, genera, and subgenera of the Eutardigrada, and keys to their identification. Zootaxa. 2404: 1-54.

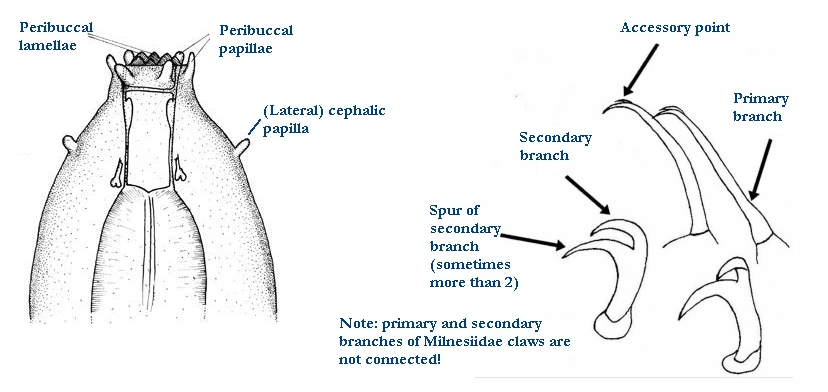
Cephalic image modified from Nelson DR, Guidetti R, Rebecchi L. 2009. Tardigrada. Ch. 14 in Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, Thorp JH, Covich AP (eds.), 3rd ed.
Claw image modified from Pilato G, Binda MG. 2010. Definition of families, subfamilies, genera, and subgenera of the Eutardigrada, and keys to their identification. Zootaxa. 2404: 1-54.
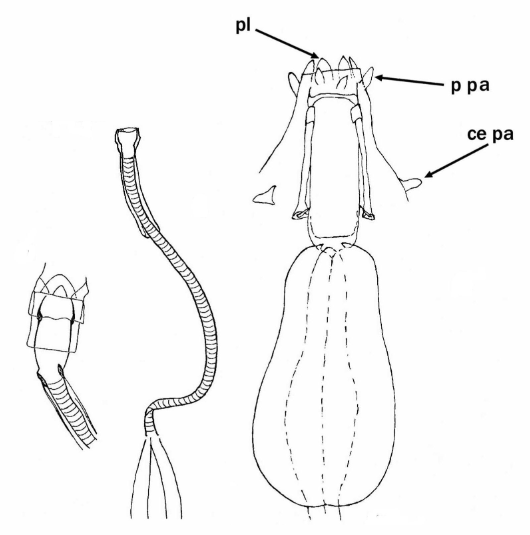
Note: in a tardigrade with snout extended, the flex of the pharyngeal tube may not be obvious.
Images from Pilato G, Binda MG. 2010. Definition of families, subfamilies, genera, and subgenera of the Eutardigrada, and keys to their identification. Zootaxa. 2404: 1-54.
Left image from Kristensen RM. 1987. Generic revision of the Echiniscidae (Heterotardigrada), with a discussion of the origin of the family. pp. 261-335 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.
Right Image from Richters F. 1926. Tardigrada. in Krumbach T. 1927. Handbuch der Zoologie, 3rd band, Walter de Gruyter & Co.
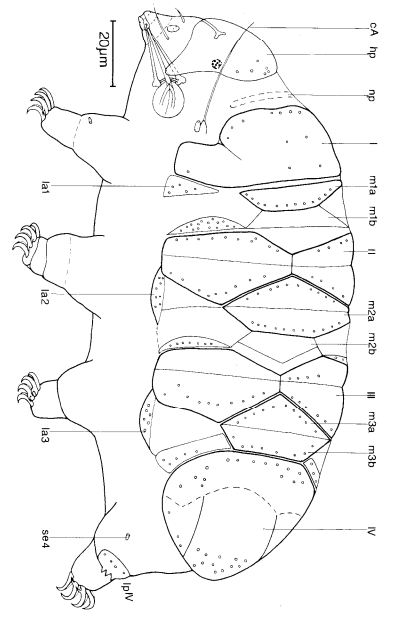
Typically papilla on leg IV (se4 in image) and variable shape on leg I
Image from Kristensen RM. 1987. Generic revision of the Echiniscidae (Heterotardigrada), with a discussion of the origin of the family. pp. 261-335 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.
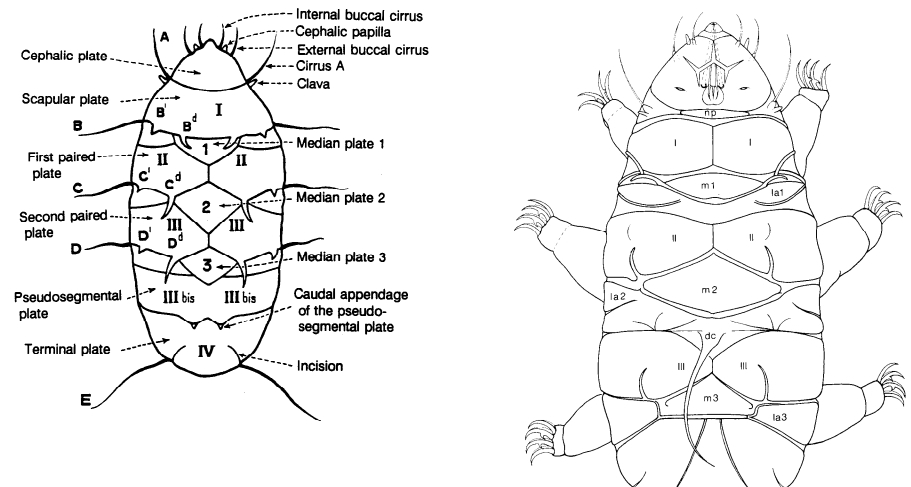
Appendages (after Cirrus A) labeled according to plate … B (Scapular plate), C (First segmental plate), D (Second segmental plate), E (terminal plate). “B” is lateral, “Bd” is dorsal
Be careful! There can be great variability within a population, with individuals (especially juveniles) lacking some appendages. When in doubt, focus on other characters first!
Left image from Ramazzotti G, Maucci W. 1983. Il phylum Tardigrada(III edizione riveduta e aggiornata). English translation by C. W. Beasley, 1995. Memorie dell’ Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia 41: 1-1012.
Right image cropped from Kristensen RM. 1987. Generic revision of the Echiniscidae (Heterotardigrada), with a discussion of the origin of the family. pp. 261-335 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.
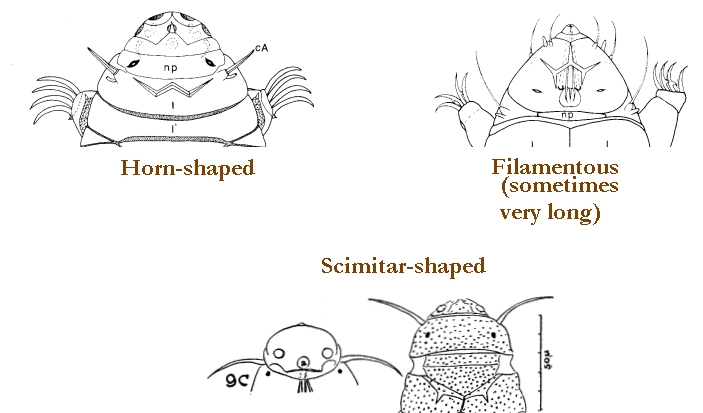
Images modified from Kristensen RM. 1987. Generic revision of the Echiniscidae (Heterotardigrada), with a discussion of the origin of the family. pp. 261-335 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.
Lower image (Mopsechiniscus) modified from du Bois-Reymond Marcus E. 1944. Sobre tardigrados brasileiros. Communicaciones Zoologicas del Museo de Historia Natural de Montevideo. 1(13): 1-19 plus plates.
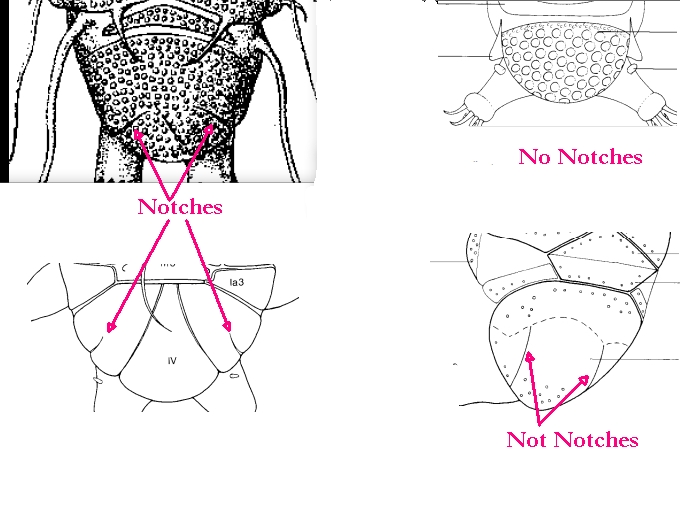
Images modified from Kristensen RM. 1987. Generic revision of the Echiniscidae (Heterotardigrada), with a discussion of the origin of the family. pp. 261-335 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.
First image (Echiniscus) modified from Richters F. 1926. Tardigrada. in Krumbach T. 1927. Handbuch der Zoologie, 3rd band, Walter de Gruyter & Co.
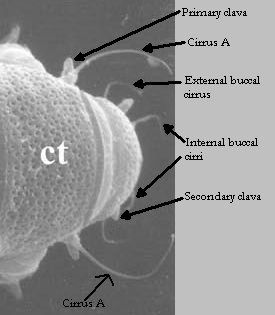
Image modified from Nelson DR, Guidetti R, Rebecchi L. 2009. Tardigrada. Ch. 14 in Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, Thorp JH, Covich AP (eds.), 3rd ed.
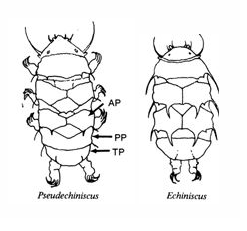
Note on 2nd image, what you see before the terminal plate is either no plate, or a full-width medial plate; don’t confuse the latter with a pseudosegmental plate!
Also, sometimes the pseudosegmental plate is paired, like segmental plates II & III. It’s still pseudosegmental!
Images from Clifford HF. 1991. Aquatic invertebrates of Alberta. University of Alberta Press, Alberta, Canada.

Image modified from Lindahl & Balser (1999), http://www.iwu.edu/~tardisdp/Keypage35.html
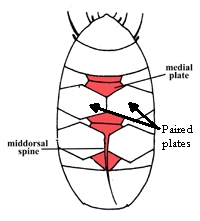
Modified from Lindahl K, Balser S. 1999. Key to tardigrade genera [Internet]. Available from: https://sun.iwu.edu/~tardisdp/Keypage33.html