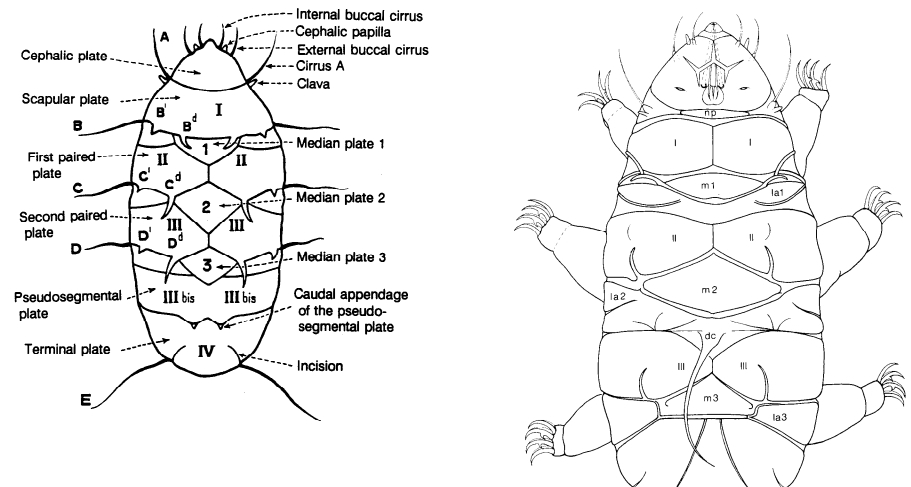
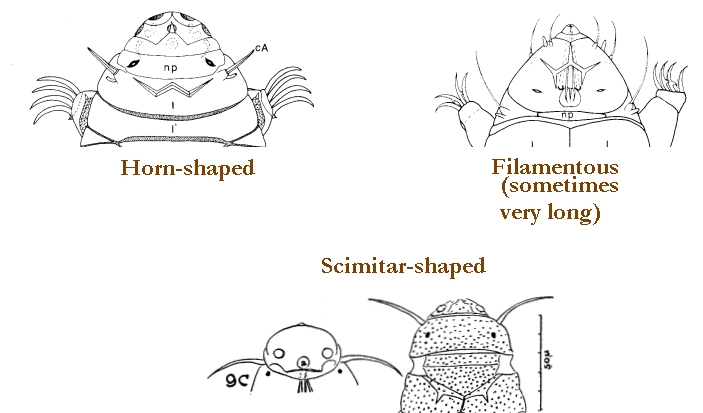
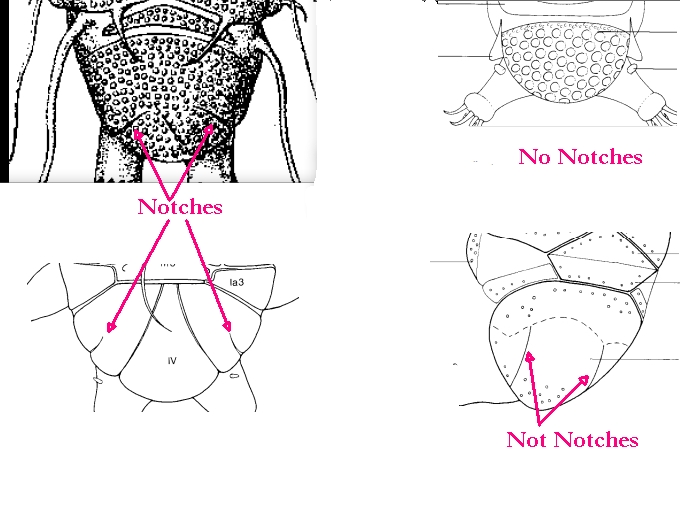
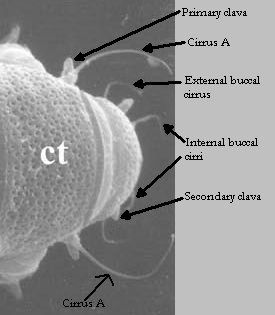
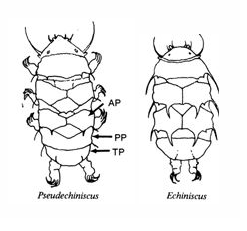
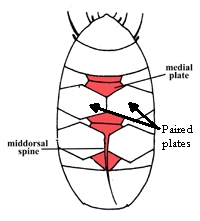
Ramazzottiidae

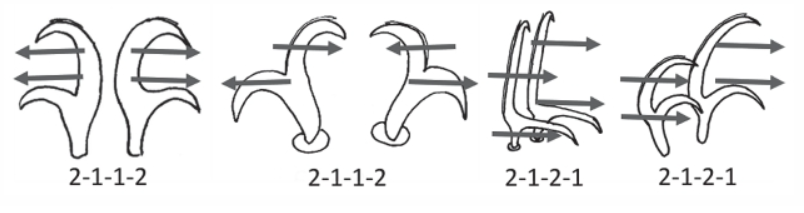
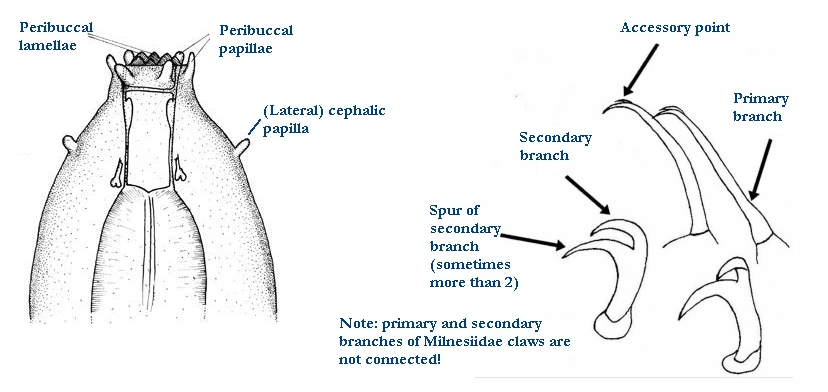
Ramazzottiidae from Marley et al. 2011: “Hypsibioidea. The AISM comprises asymmetric, dissimilar dorsal and ventral ‘blunt hooks’. Claw pairs asymmetric (2121), external claw primary branch joins the secondary claw and basal section with flexible junction; primary branch may be very long and slender; the internal claw branches and basal section unified into a single rigid element. Eggs […]
Pilatobiidae

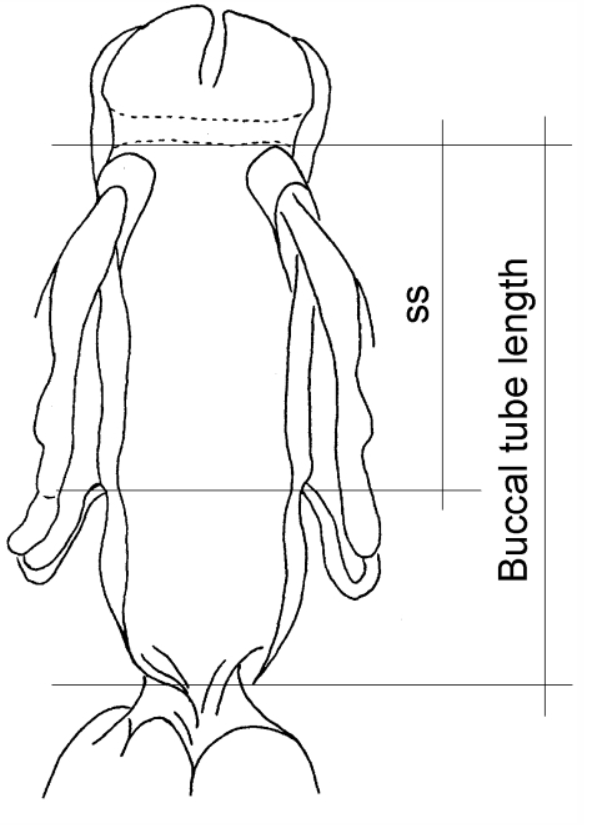
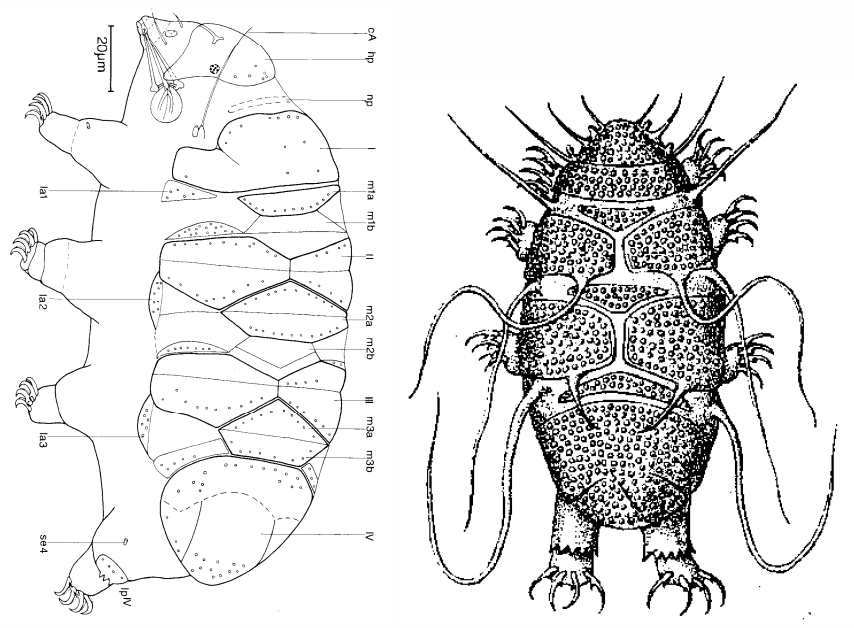
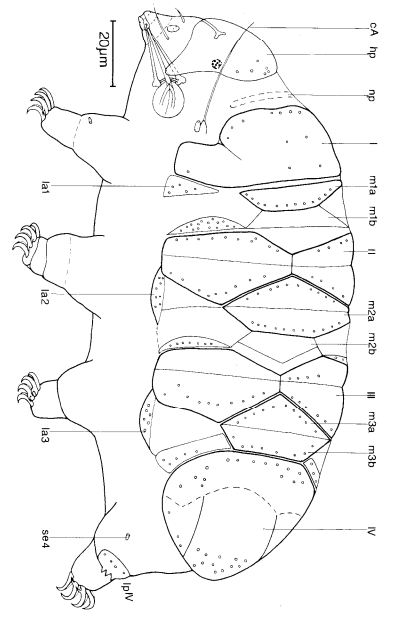
Formerly Pilatobiinae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Buccal tube followed by an annulated pharyngeal tube, with a drop-like thickening between them; pharyngeal bulb roundish or slightly oval, always containing 2 macroplacoids similar in length and in rows that look as parentheses, and a septulum.” The subfamily Pilatobiinae no longer exists, as it was promoted to the family […]
Microhypsibiidae

Microhypsibiidae from Pilato 1998: “Eutardigrades having claws arranged asymmetrically with respect to the median plane of the legs. Claws of Microhypsibius type: the claws have a narrow basal portion continuous with the primary branch; the secondary branch is rigidly joined to the primary branch. The internal claws cannot rotate on their bases.” Microhypsibiidae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double […]
Itaquasconidae

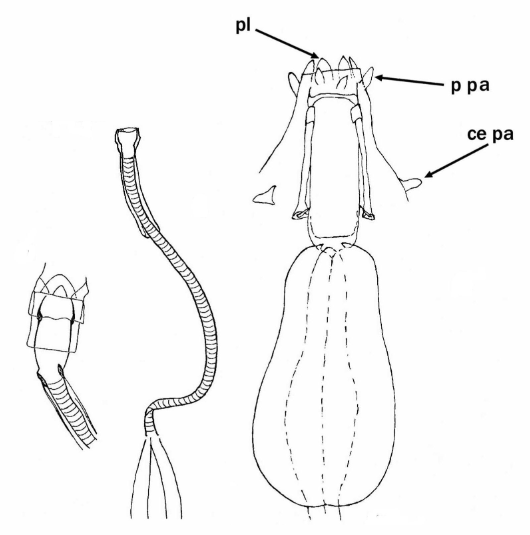
Formerly Itaquasconinae from Pilato 1969: “Unghie di tipo Hypsibius; apparato boccale di tipo Diphascon; placoidi presenti o assenti.” Translated: Claws of Hypsibius type; buccal apparatus of Diphascon type; placoids present or absent. Formerly Itaquasconinae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Buccal tube followed by a flexible portion, without cuticular thickening between them; the flexible portion is an annulated pharyngeal tube in all genera (Parascon excluded); […]
Hypsibiinae

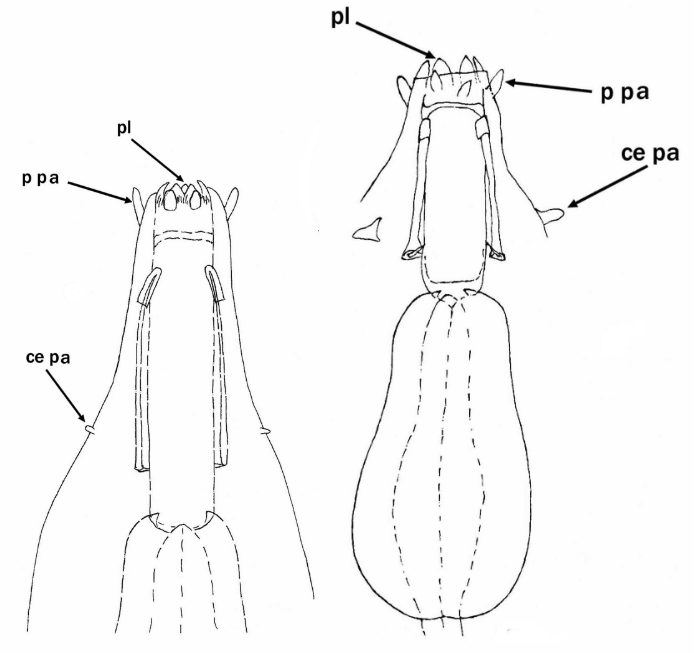
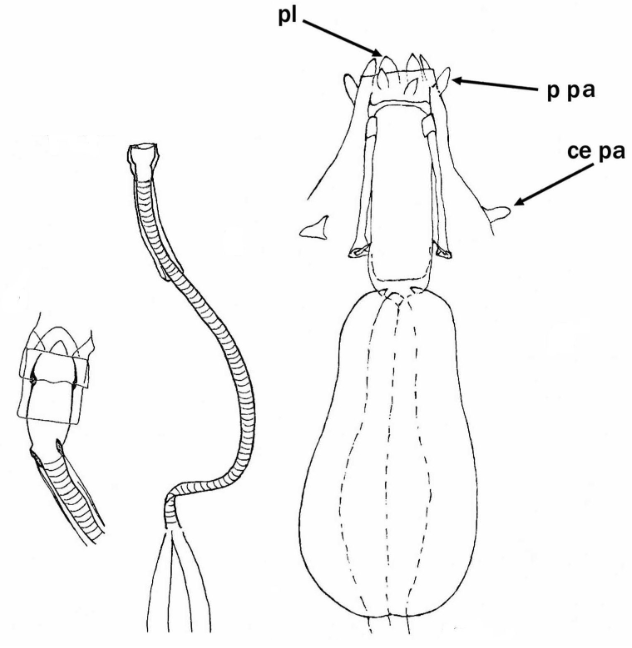
Hypsibiinae from Pilato 1969: “Unghie di tipo Isohypsibius o di tipo Hypsibius. Apparato boccale di tipo Hypsibius o di tipo Macrobiotus; bulbo faringeo provvisto di placoidi.” Translated: Claws of Isohypsibius or Hypsibius type. Buccal apparatus of Hypsibius or Macrobiotus type; pharyngeal bulb with placoids. Hypsibiinae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Completely rigid buccal tube. Apophyses […]
Diphasconinae

“Eutardigrades with buccopharyngeal apparatus of Diphascon-type and anterior apophyses shaped as “blunt” or “semilunar” hooks (see Pilato 1987). Posteriodorsal apodeme (“drop-like” structure) present or absent, pharyngeal apophyses present. Asymmetrical claws of Hypsibiidae-type. Eggs either deposited into [shedded] cuticle and smooth or layed freely and with ornamented shells.” Dastych H. 1992. Paradiphascon manningi gen. n. sp. […]
Hypsibiidae

Hypsibiidae from Pilato 1969: “Senza alcuna appendice cefalica. Le due diplounghie di ciascuna zampa sono disposte asimmetricamente rispetto al piano mediano della zampa stessa e posssono essere di tipo Isohypsibius o di tipo Hypsibius. In ogni zampa le due diplounghie sono talvolta quasi uguali fra loro ma molto spesso profondamente diverse per forma e dimensioni. […]
Calohypsibiidae

Calohypsibiidae from Pilato 1969: “Senza alcuna appendice cefalica. Le due diplounghie di ciascuna zampa sono disposte asimmetricamente rispetto al piano mediano della zampa stessa e sono di tipo Calohypsibius. In ogni zampa le due diplounghie sono uguali per forma e poco diverse fra loro per dimensioni; finora non si conoscono specie provviste di lunule. (La […]
Acutuncidae

Hypsibioidea

Hypsibioidea from Pilato 1969 in Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela; claws asymmetrical (2121); Hypsibius-type claw pairs; AISM hooked (or, if the buccal tube is elongated, AISM can be broad ridges).” Hypsibioidea from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws asymmetrical with respect to the median plane of the leg (2121), the external (or posterior) claw often with flexible main branch; double claws […]