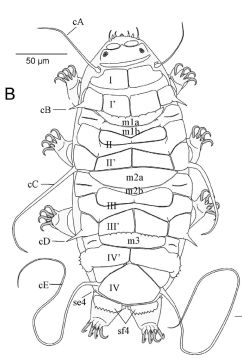
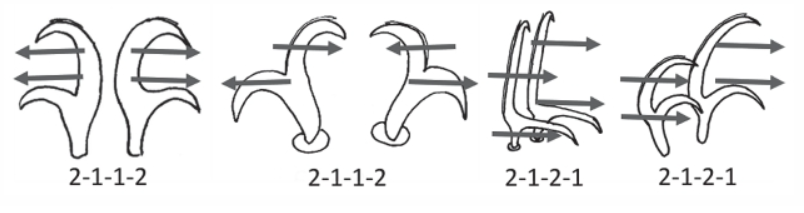
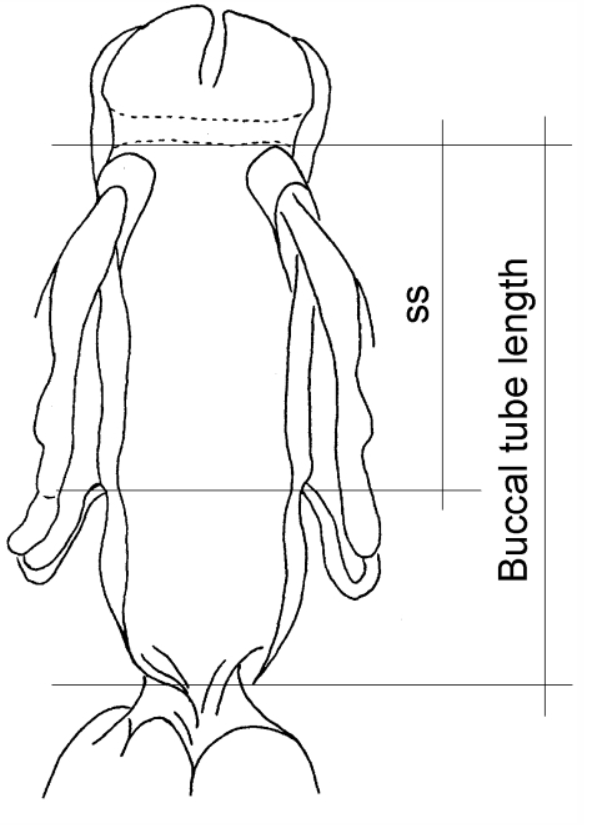
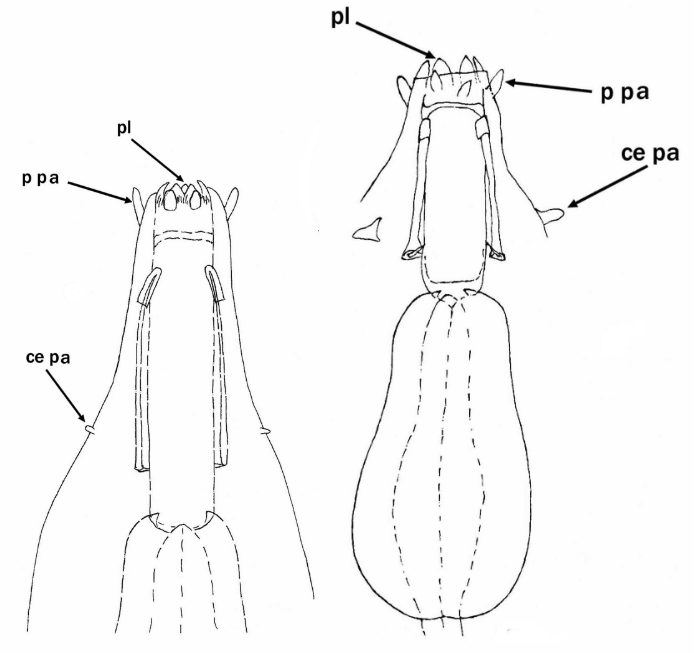
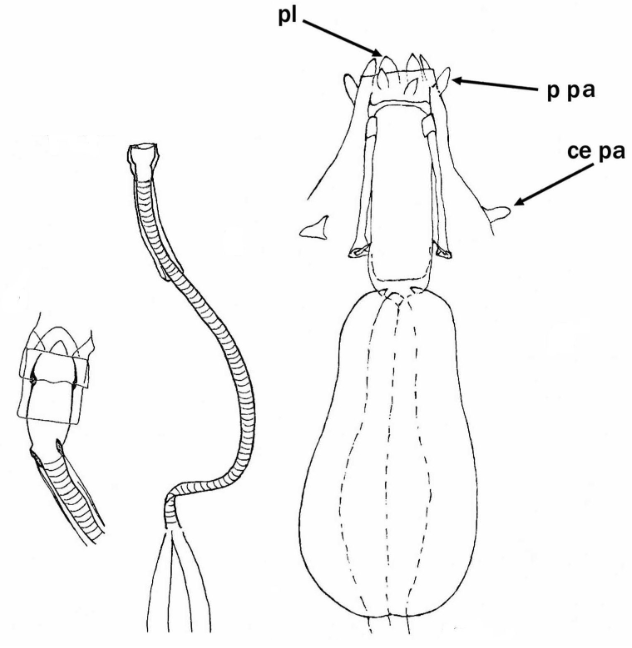
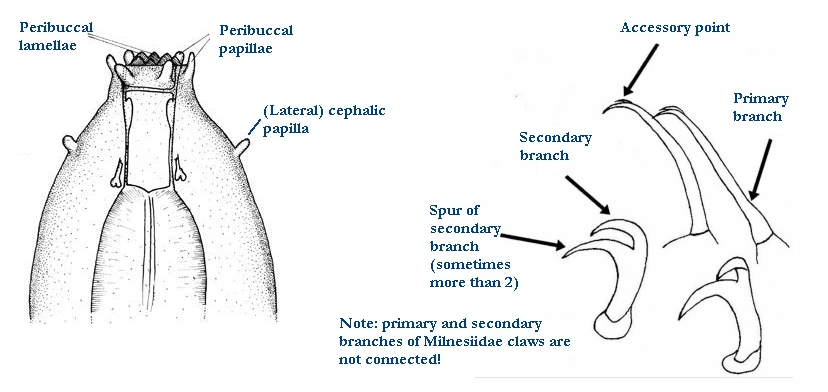
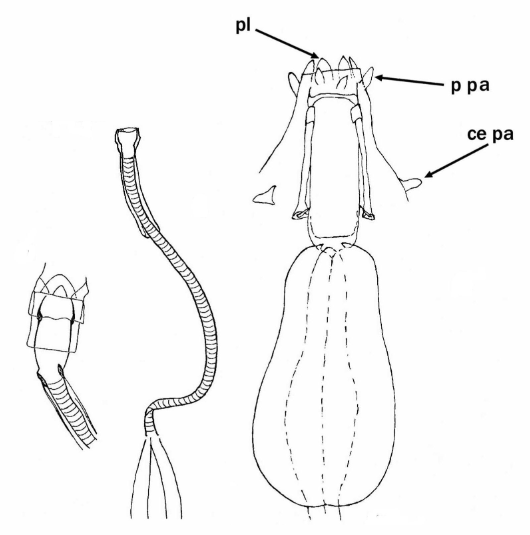
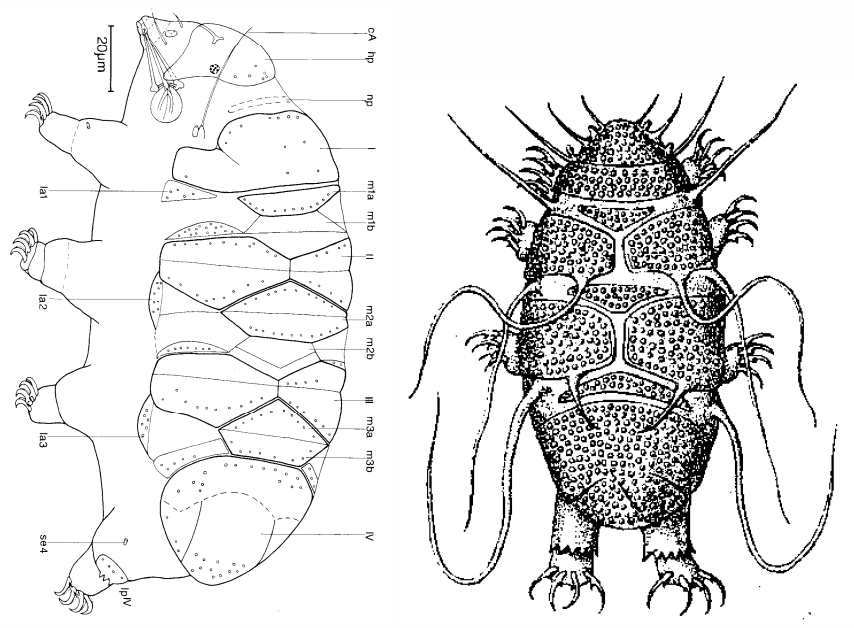
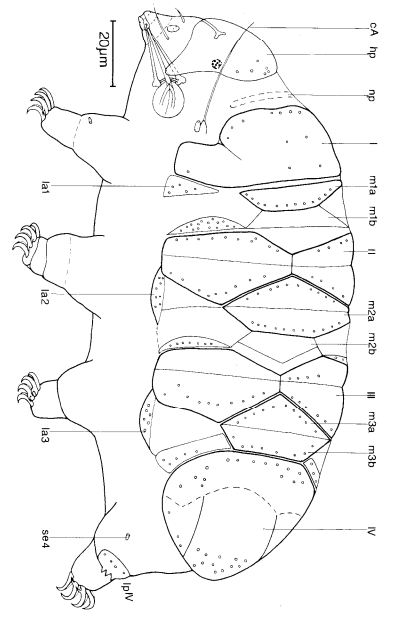
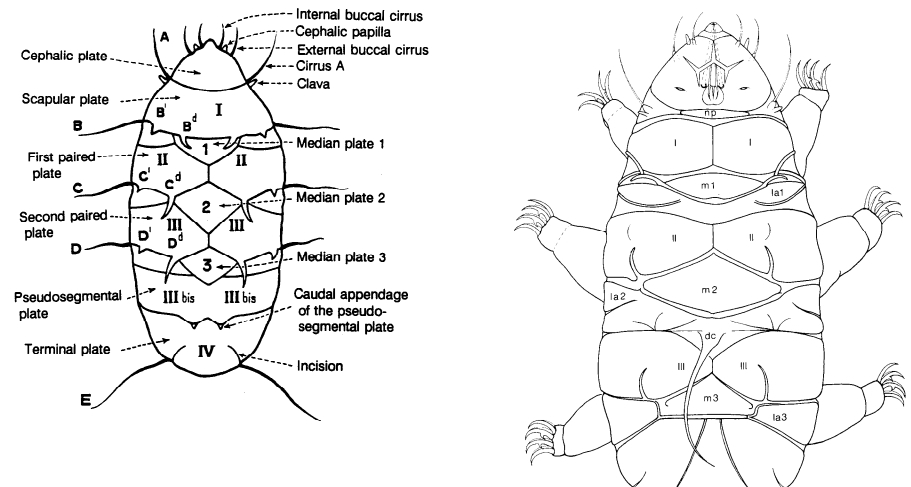
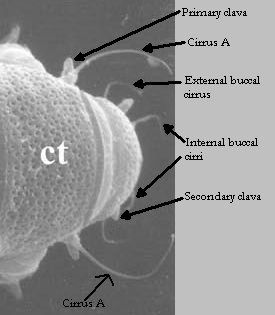
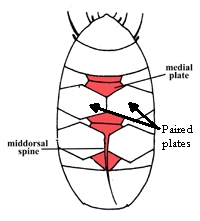
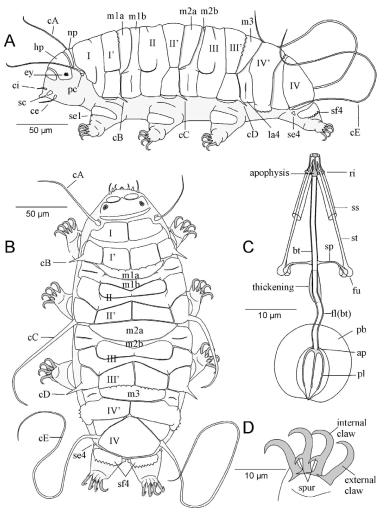
From Miller, Schulte, Johansson 2012: “Echiniscidae with dorsal segmental plates, pseudosegmental plates, and without ventral plates. Each segmental plate divided into two or more pieces, one or more piece paired. Anterior piece of cephalic and scapular plates paired. Posterior piece of trunk segment plates I, II, and III paired, forming pseudosegmental plates. Terminal plate divided into three pieces. Median plates 1 and 2 divided. Median plate 3 undivided. Lateral intersegmental plates present. Elongated buccal apparatus. Long, flexible stylet sheaths. Bulb shaped buccal apophysis for muscle attachment present. Anterior portion of buccal tube rigid, thin stylet supports attach about midpoint and anterior to buccal tube thickening. Posterior part of buccal tube flexible. Robust spurs on the internal claws.
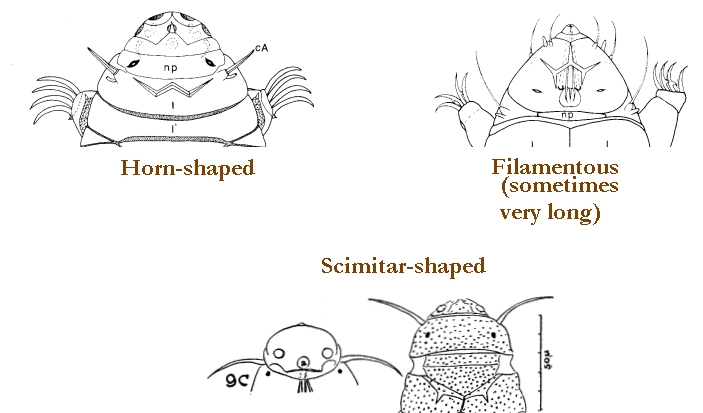
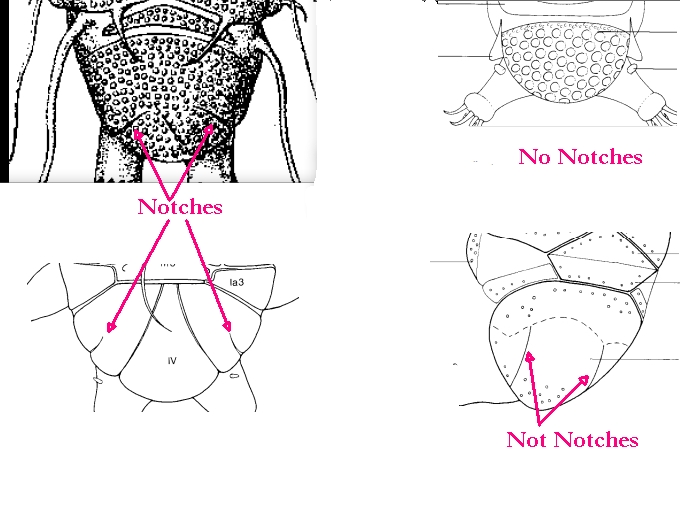
Comparisons: A long, flexible buccal tube is not a characteristic of Pseudechiniscus but is found in Novechiniscus, Proechiniscus, Cornechiniscus, and Mopsechiniscus. Multipseudechiniscusis not Novechiniscus nor Proechiniscus, which lack paired segmental plates. Multipseudechiniscus is not Mopsechiniscus because Multipseudechiniscus has internal and external cirri lacking in Mopsechiniscus. While the arrangement of the dorsal plates most closely resembles Cornechiniscus, cirrus A is filamentous not a thick horn or spike. In addition, pseudosegmental plates II’ and III’ are unpaired on Cornechiniscus and paired on Multipseudechiniscus.”
Citations:
Miller WR, Schulte R, Johansson C. 2012. Tardigrades of North America: further description of the genus Multipseudechiniscus Schulte and Miller, 2011 (Heterotardigrada: Echiniscoidea: Echiniscidae) from California. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 125(2): 153-164.