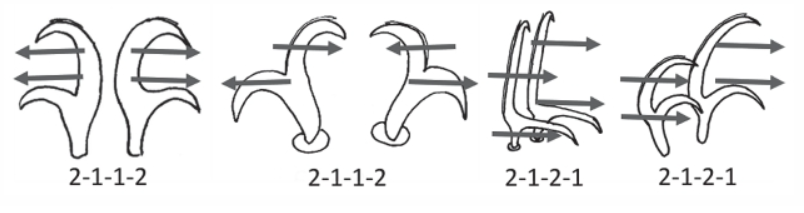
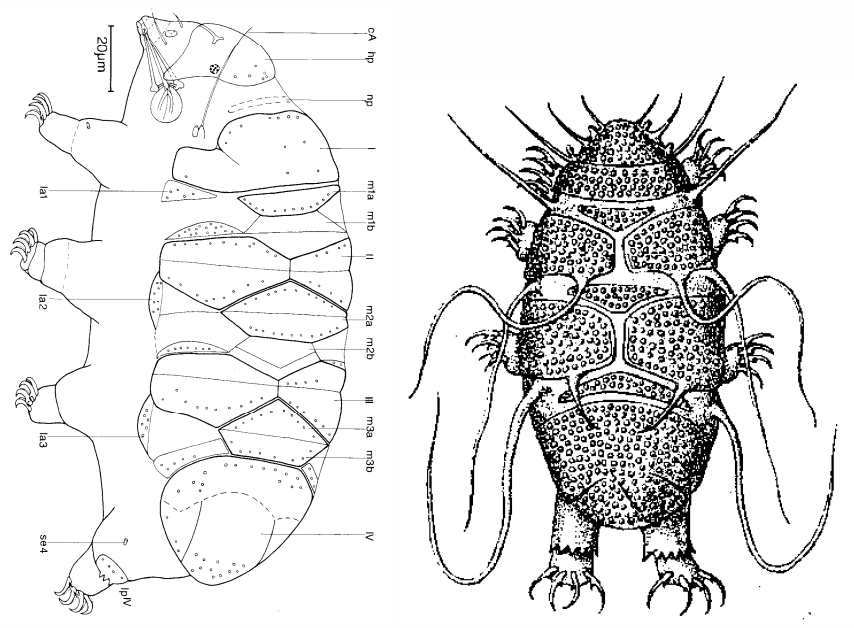
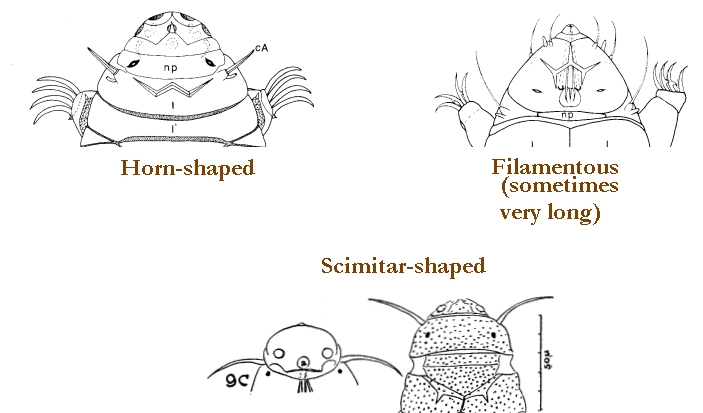
Hypsibioidea from Pilato 1969 in Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela; claws asymmetrical (2121); Hypsibius-type claw pairs; AISM hooked (or, if the buccal tube is elongated, AISM can be broad ridges).”
Hypsibioidea from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws asymmetrical with respect to the median plane of the leg (2121), the external (or posterior) claw often with flexible main branch; double claws different in size and shape on the same leg (Hypsibius and Ramazzottius type, or modified), or very reduced in size (Calohypsibius and Microhypsibius type); buccal tube often very narrow”
Hypsibioidea from Gąsiorek et al. 2018: “Eutardigrades with asymmetrical claws (2-1-2-1) and pseudolunulae at claw bases or without any cuticular structures under the basal parts. Hooked or broad-ridged apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles. Herbivorous or microbivorous (Guidetti et al. 2012).”
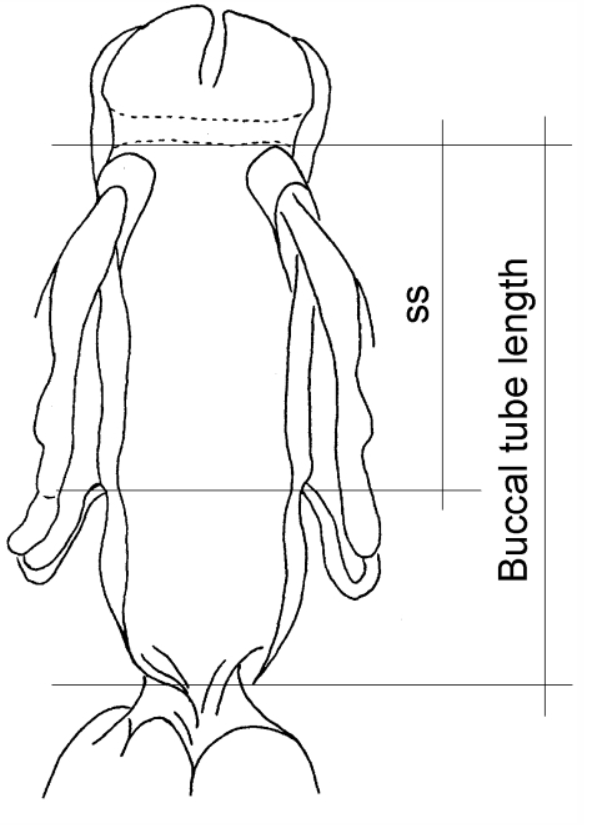
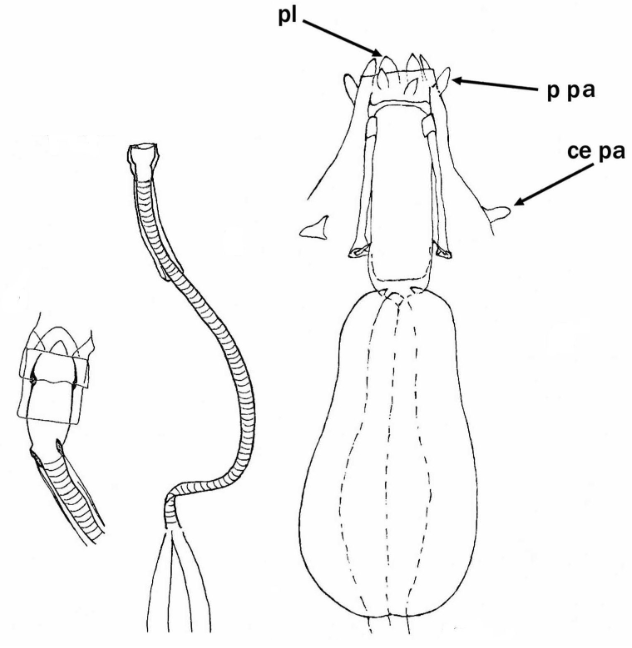
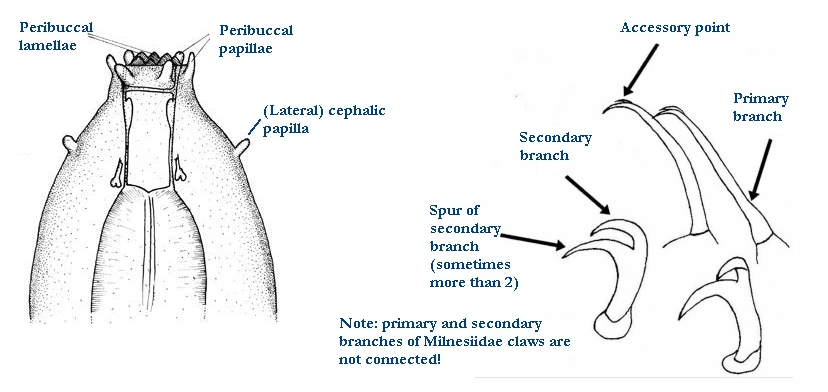
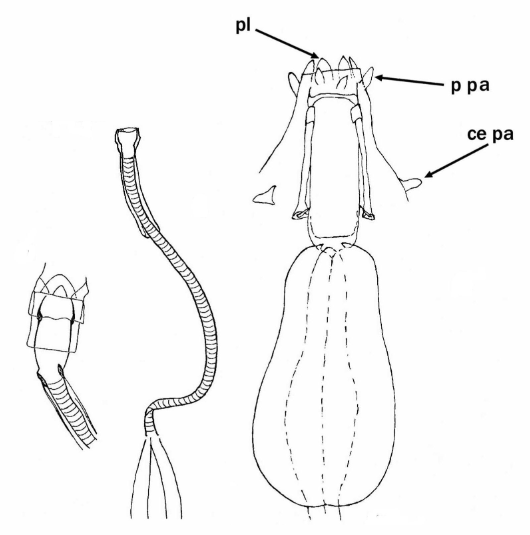
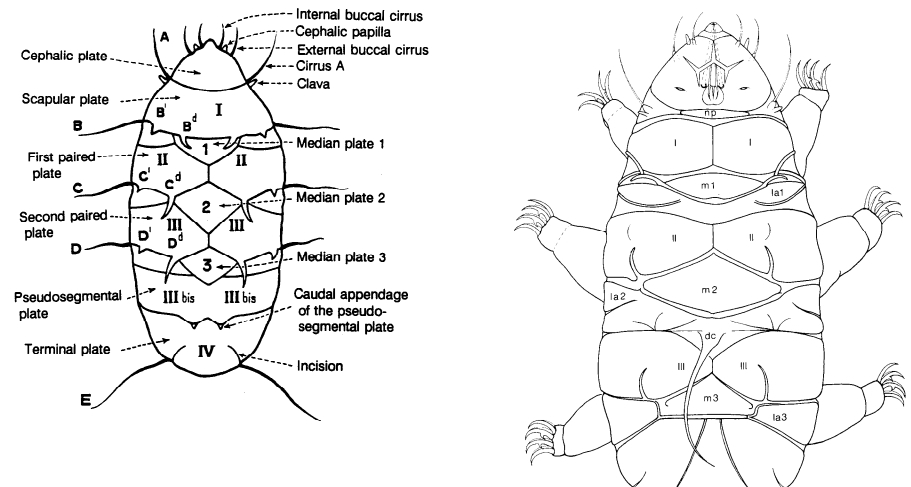
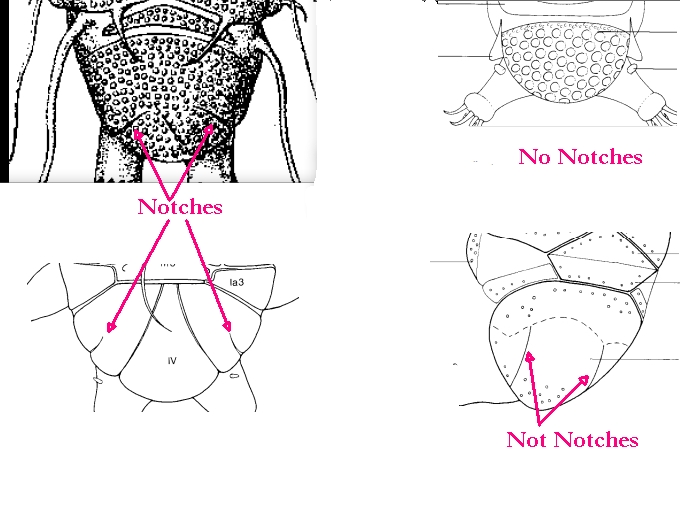
Ramazzottiidae from Marley et al. 2011: “Hypsibioidea. The AISM comprises asymmetric, dissimilar dorsal and ventral ‘blunt hooks’. Claw pairs asymmetric (2121), external claw primary branch joins the secondary claw and basal section with flexible junction; primary branch may be very long and slender; the internal claw branches and basal section unified into a single rigid element. Eggs have a sculptured chorion and are deposited free in the environment.”
Ramazzottiidae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws different in shape and size on the same leg, the external (or posterior) claw with the primary branch connected to basal tract with an evident, thin, flexible tract (Ramazzottius or oberhaeuseri type, or modified), or completely disconnected. Eggs laid freely and with ornamented shell.”
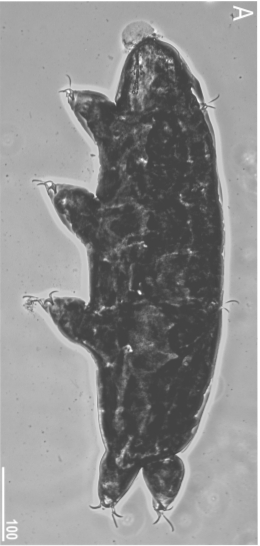
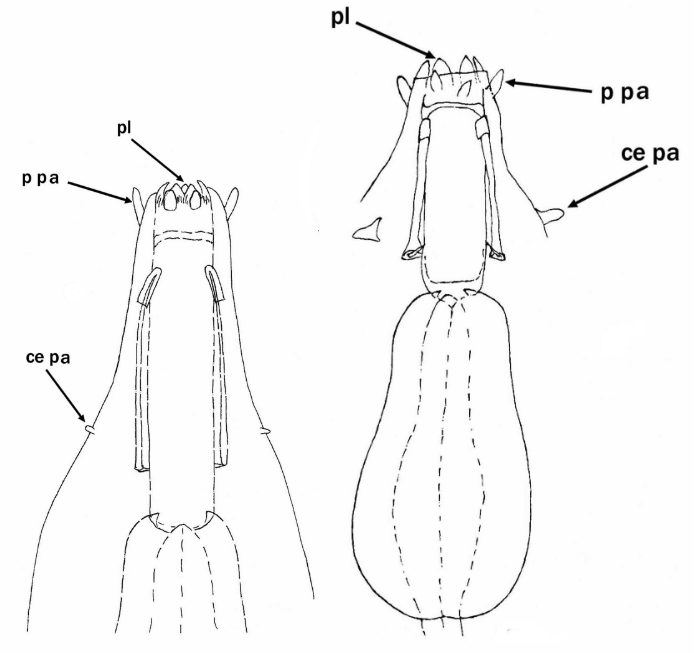
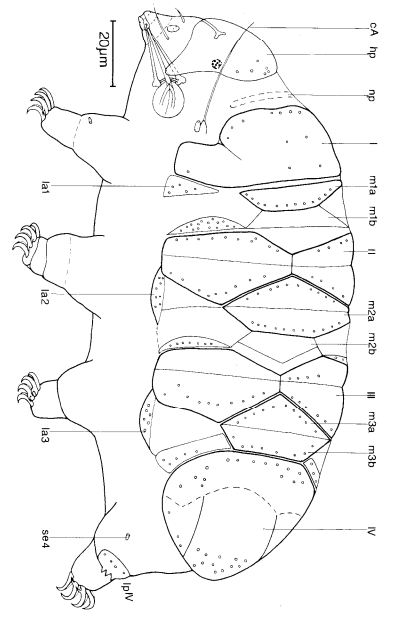
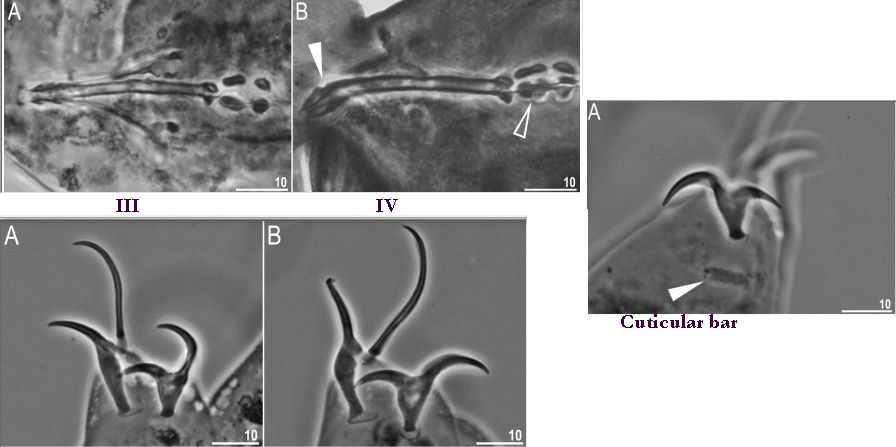
Genus description from Zawierucha et al. 2018: “Juveniles light-brown, adults intensely dark-brown. Peribuccal lamellae and papulae absent. Buccal apparatus of the Ramazzottius type, with asymmetrical apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles and two macroplacoids; microplacoid and septulum absent. Claws of the Ramazzottius type, but without accessory points. The posterior primary branch almost uniform in diameter from the base to the curving. Wide, semi-transparent cuticular bars under claws I–III.”
Citations :
Bertolani R, Guidetti R, Marchioro T, Altiero T, Rebecchi L, Cesari M. 2014. Phyloeny of Eutardigrada: New molecular data and their morphological support lead to the identification of new evolutionary lineages. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 76: 110-126.
Gąsiorek P, Stec D, Morek W, Michalczyk Ł. 2018. An integrative redescription of Hypsibius dujardini (Doyère, 1840), the nominal taxon for Hypsibioidea (Tardigrada: Eutardigrada). Zootaxa. 4415 (1): 45-75.
Marley NJ, McInnes SJ, Sands CJ. 2011. Phylum Tardigrada: A re-evaluation of the Parachela. Zootaxa. 2819: 51-64.
Pilato G. 1969. Schema per una nuova sistemazione delle famiglie e dei generi degli Eutardigrada. Bollettino delle Sedute della Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali in Catania, Series IV. 10 (277): 181-193.
Zawierucha K, Stec D, Lachowska-Cierlik D, Takeuchi N, Li Z, Michalczyk Ł. 2018. High mitochondrial diversity in a new water bear species (Tardigrada: Eutardigrada) from mountain glaciers in central Asia, with the erection of a new genus Cryoconicus. Annales Zoologici. 68 (1): 179-201.