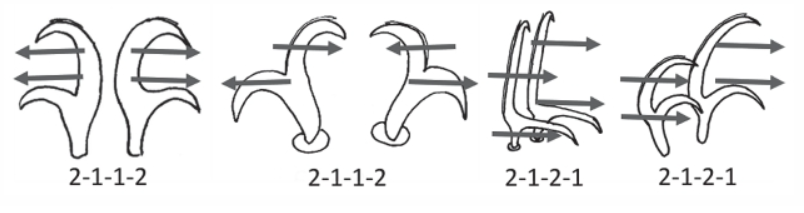
Hypsibioidea from Pilato 1969 in Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela; claws asymmetrical (2121); Hypsibius-type claw pairs; AISM hooked (or, if the buccal tube is elongated, AISM can be broad ridges).”
Hypsibioidea from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws asymmetrical with respect to the median plane of the leg (2121), the external (or posterior) claw often with flexible main branch; double claws different in size and shape on the same leg (Hypsibius and Ramazzottius type, or modified), or very reduced in size (Calohypsibius and Microhypsibius type); buccal tube often very narrow”
Hypsibioidea from Gąsiorek et al. 2018: “Eutardigrades with asymmetrical claws (2-1-2-1) and pseudolunulae at claw bases or without any cuticular structures under the basal parts. Hooked or broad ridged apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles. Herbivorous or microbivorous (Guidetti et al. 2012).”
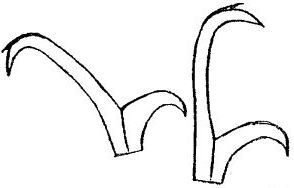
Calohypsibiidae from Pilato 1969: “Senza alcuna appendice cefalica. Le due diplounghie di ciascuna zampa sono disposte asimmetricamente rispetto al piano mediano della zampa stessa e sono di tipo Calohypsibius. In ogni zampa le due diplounghie sono uguali per forma e poco diverse fra loro per dimensioni; finora non si conoscono specie provviste di lunule. (La disposizione asimmetrica delle diplounghie e la loro struttura possono non essere evidenti in specie del genere Haplomacrobiotus ove il ramo secondario può ridursi fino a scomparire; in tal caso ogni zampa sembra portare due unghie semplici invece di due diplounghie).”
Translated: Without any cephalic appendages. The two double-claws of each leg are arranged asymmetrically with respect to the median plane of the leg and are of the Calohypsibius type. On each leg the two double-claws are identical in shape and not very different in size; so far there are no known species with lunulae.
(The asymmetric arrangement of the double-claws and their structure may not be evident in species of the genus Haplomacrobiotus where the secondary branch may be reduced to nothing; in this case, each leg appears to carry two simple claws instead of two double-claws).
Calohypsibiidae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws of the Calohypsibius type (small, rigid, in frontal view with a base as large as the sum of the primary and secondary branch widths, but without a suture between the two branches); double claws similar in size and shape on the same leg; buccal tube completely rigid; apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles on the buccal tube asymmetrical with respect to the frontal plane.”
Genus description from Thulin 1928: “Krallen vom ersten Typus. Placoidenreihen des Schlundkopfes kurz, jede a u s zwei kurzen Macroplacoiden bestehend. Mundröhre sehr eng, beim Eintritt in den Schlundkopf gebogen. Der Körper mit Querreihen von Dornen oder Warzen versehen.”
Translated: Claws of the first [Calohypsibius/Microhypsibius] type. Placoid rows of the pharynx short, each consisting of two short macroplacoids. Mouth tube very tight, bent on entry into the pharynx. The body is provided with transverse rows of thorns (spines) or warts (tubercles).”
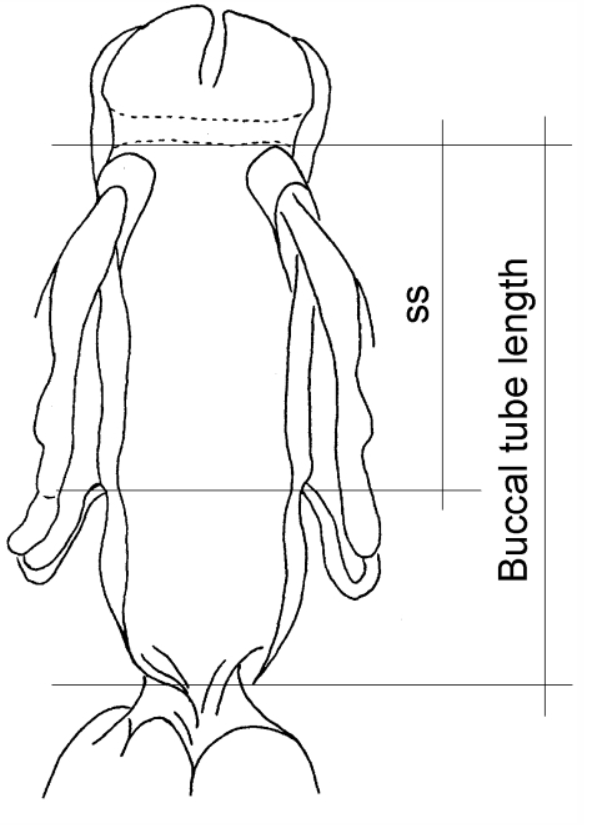
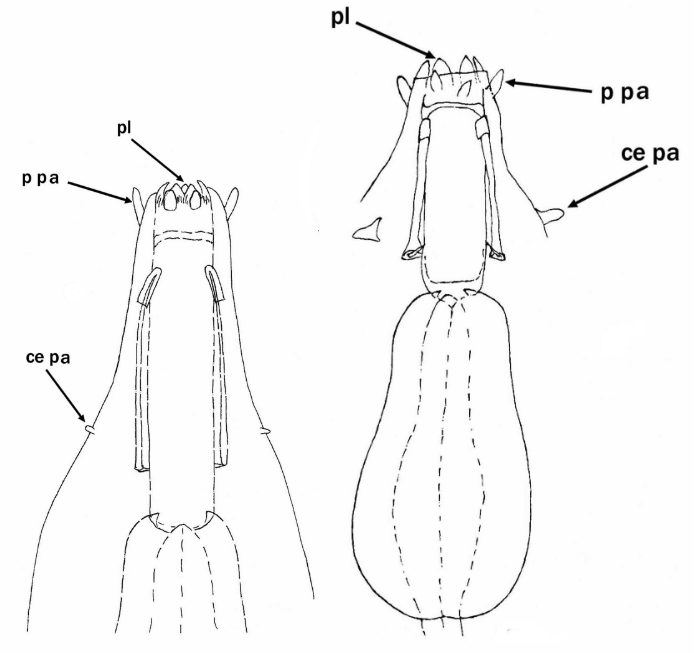
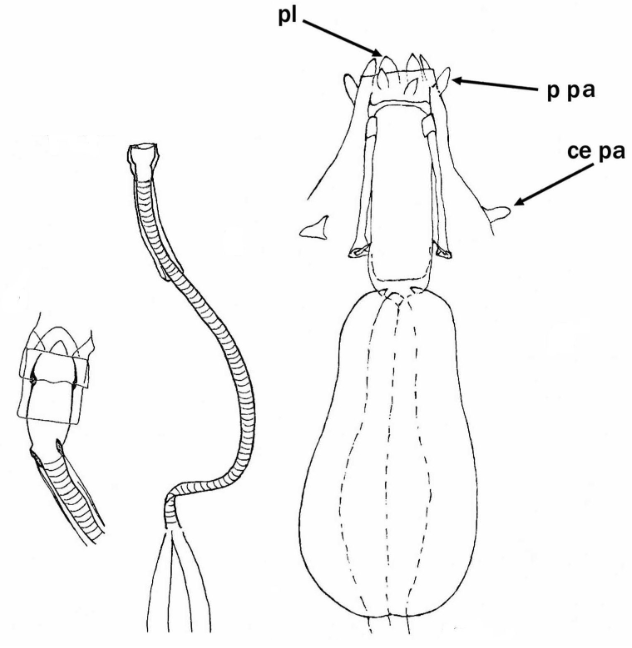
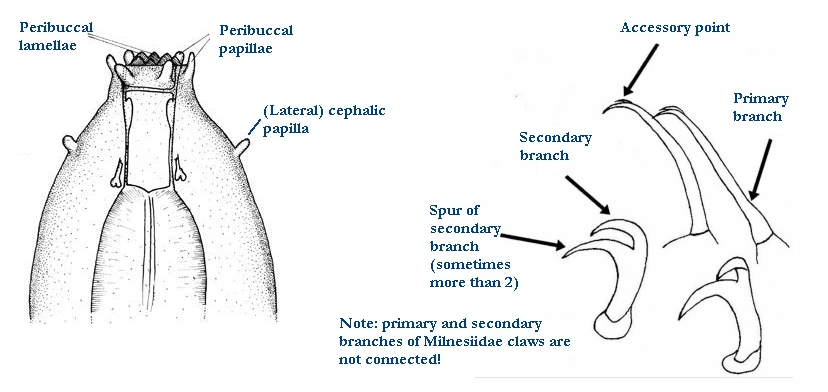
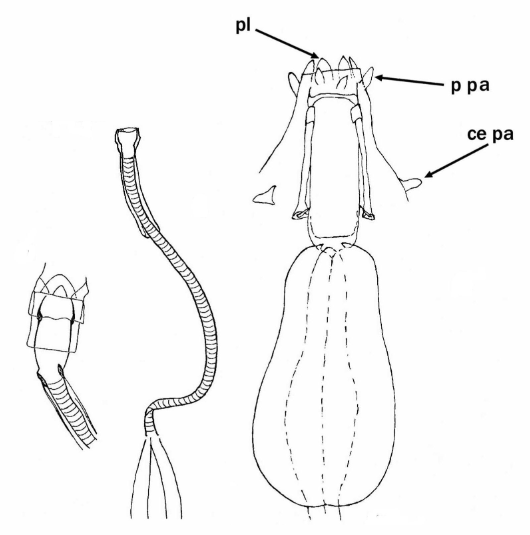
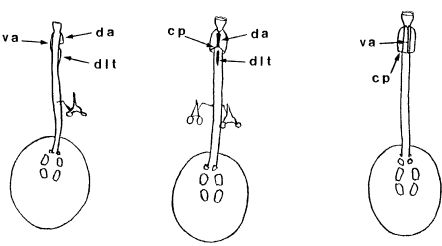
Genus description from Michalczyk & Kaczmarek 2005: “…rigid buccal tube with one bend in the posterior portion and without the ventral lamina. Apophyses for the stylet muscles insertion are asymmetrical in the lateral view (the ventral apophysis is in the shape of a very low ridge, while the dorsal apophysis is split into two portions: an anterior stumpy hook with a blunt caudal apex and a posterior short longitudinal thickening). The mouth opening is antero-ventral, with six peribuccal papulae. Claws (with 2-1-2-1 sequence) are small, rigid, and similar in size and shape. The claw branches are rigidly connected and the main branches have small accessory points.
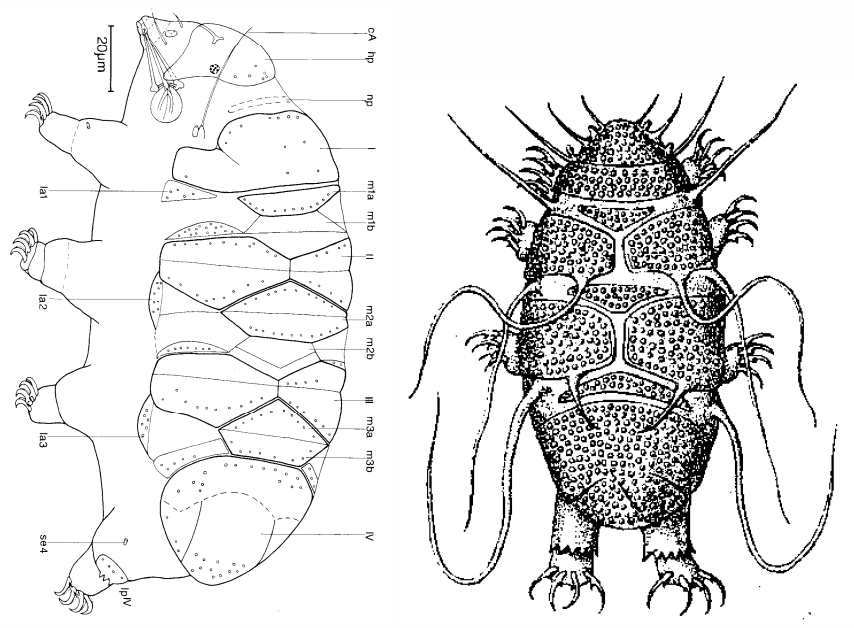
All known species within the genus have a small body size (up to 250.0 µm) with a distinctly sculptured dorsal cuticle with tubercles and some also with spines.”
Citations:
Bertolani R, Guidetti R, Marchioro T, Altiero T, Rebecchi L, Cesari M. 2014. Phyloeny of Eutardigrada: New molecular data and their morphological support lead to the identification of new evolutionary lineages. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 76: 110-126.
Gąsiorek P, Stec D, Morek W, Michalczyk Ł. 2018. An integrative redescription of Hypsibius dujardini (Doyère, 1840), the nominal taxon for Hypsibioidea (Tardigrada: Eutardigrada). Zootaxa. 4415 (1): 45-75.
Marley NJ, McInnes SJ, Sands CJ. 2011. Phylum Tardigrada: A re-evaluation of the Parachela. Zootaxa. 2819: 51-64.
Michalczyk Ł, Kaczmarek Ł. 2005. The first record of the genus Calohypsibius Thulin, 1928 (Eutardigrada: Calohypsibiidae) from Chile (South America) with a description of a new species Calohypsibius maliki. New Zealand Journal of Zoology. 32: 287-292.
Pilato G. 1969. Schema per una nuova sistemazione delle famiglie e dei generi degli Eutardigrada. Bollettino delle Sedute della Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali in Catania, Series IV. 10 (277): 181-193.
Thulin G. 1928. Über die phylogenie und das system der tardigraden. Zoologisches Institut, Lund.