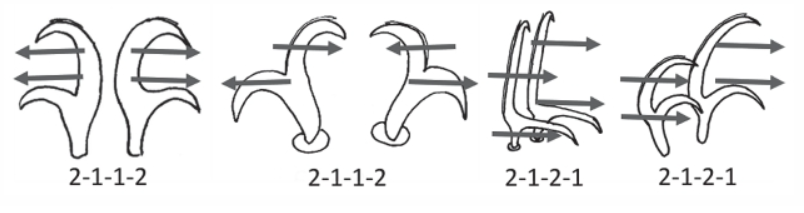
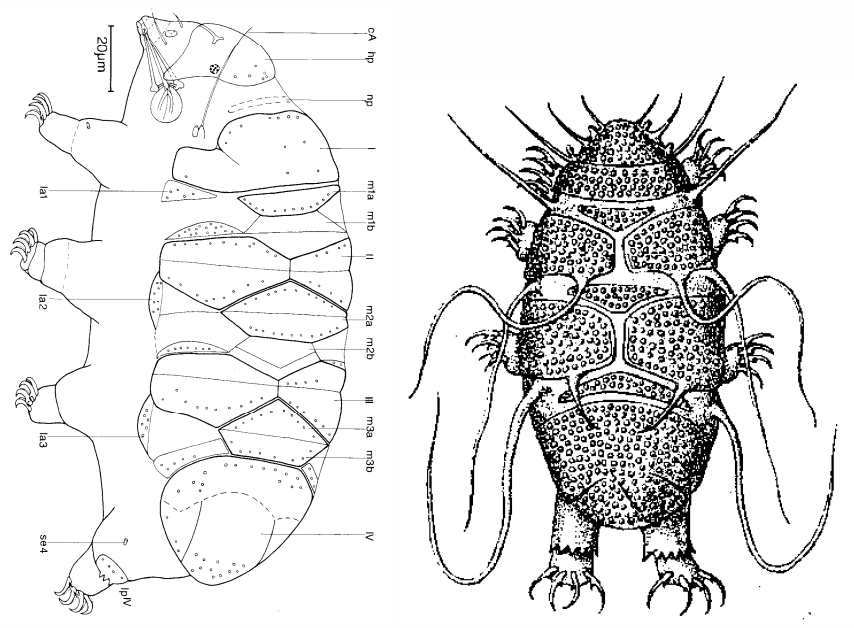
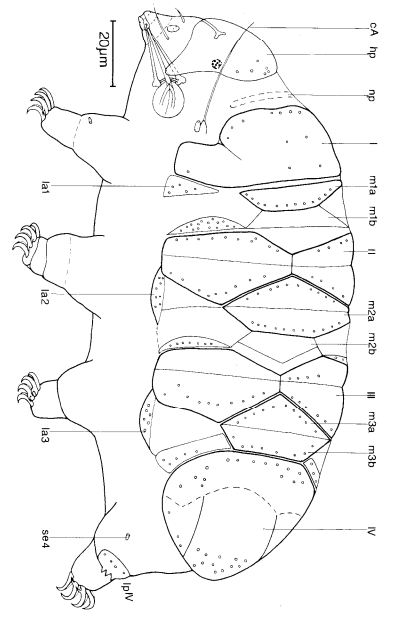
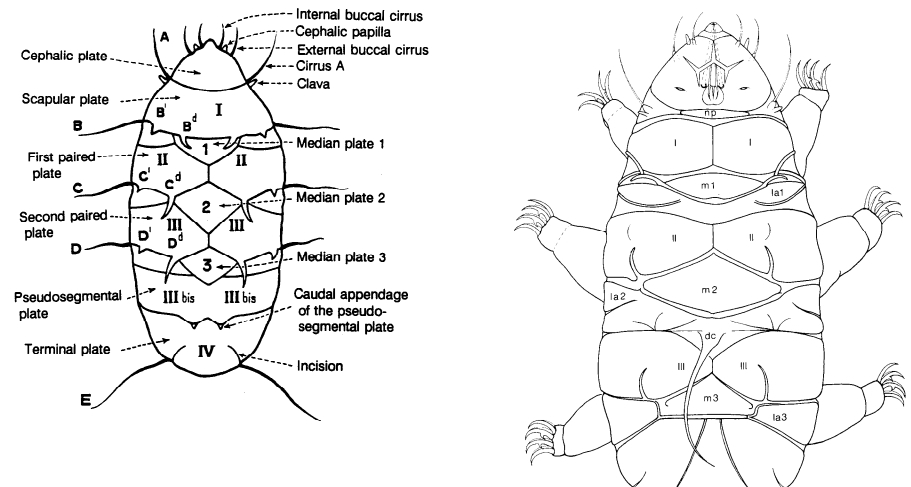
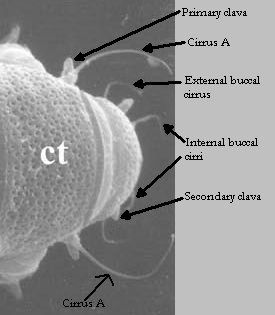
Hypsibioidea from Pilato 1969 in Marley et al. 2011: “Parachela; claws asymmetrical (2121); Hypsibius-type claw pairs; AISM hooked (or, if the buccal tube is elongated, AISM can be broad ridges).”
Hypsibioidea from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws asymmetrical with respect to the median plane of the leg (2121), the external (or posterior) claw often with flexible main branch; double claws different in size and shape on the same leg (Hypsibius and Ramazzottius type, or modified), or very reduced in size (Calohypsibius and Microhypsibius type); buccal tube often very narrow”
Hypsibioidea from Gąsiorek et al. 2018: “Eutardigrades with asymmetrical claws (2-1-2-1) and pseudolunulae at claw bases or without any cuticular structures under the basal parts. Hooked or broad-ridged apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles. Herbivorous or microbivorous (Guidetti et al. 2012).”
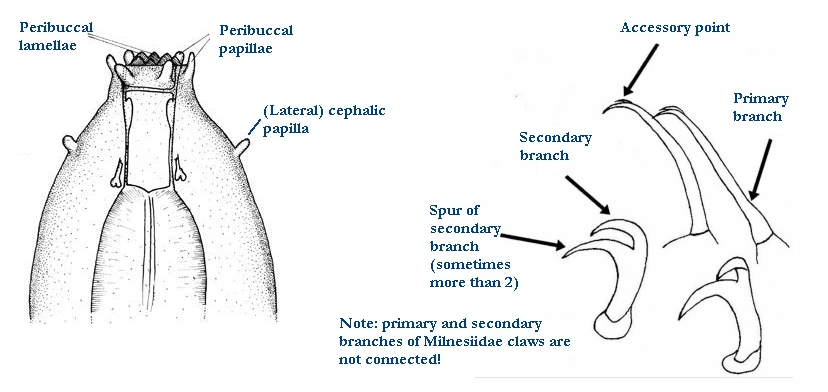
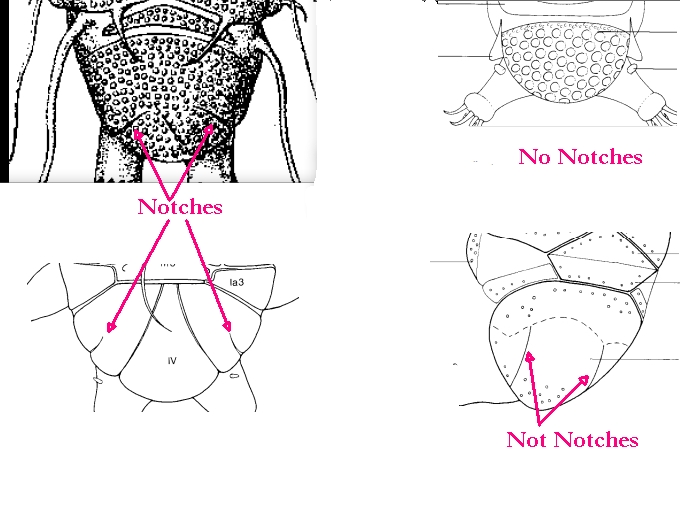
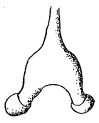
Ramazzottiidae from Marley et al. 2011: “Hypsibioidea. The AISM comprises asymmetric, dissimilar dorsal and ventral ‘blunt hooks’. Claw pairs asymmetric (2121), external claw primary branch joins the secondary claw and basal section with flexible junction; primary branch may be very long and slender; the internal claw branches and basal section unified into a single rigid element. Eggs have a sculptured chorion and are deposited free in the environment.”
Ramazzottiidae from Bertolani et al. 2014: “Double claws different in shape and size on the same leg, the external (or posterior) claw with the primary branch connected to basal tract with an evident, thin, flexible tract (Ramazzottius or oberhaeuseri type, or modified), or completely disconnected. Eggs laid freely and with ornamented shell.”
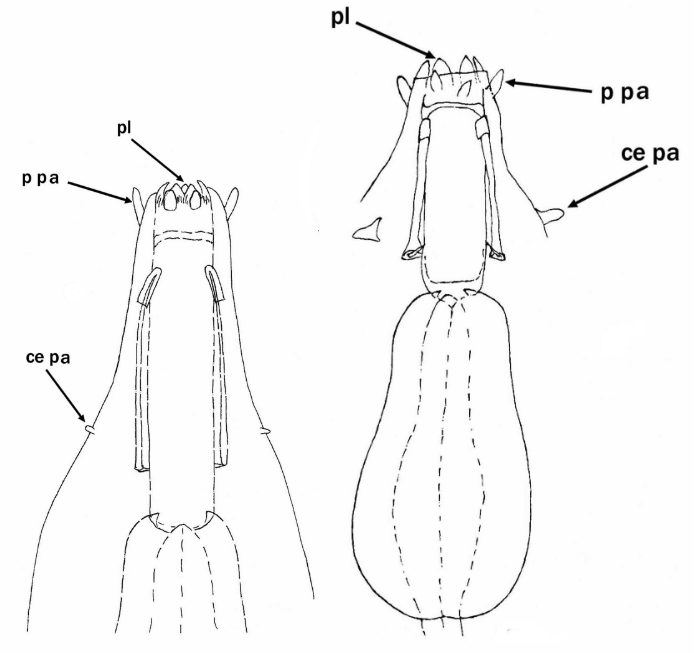
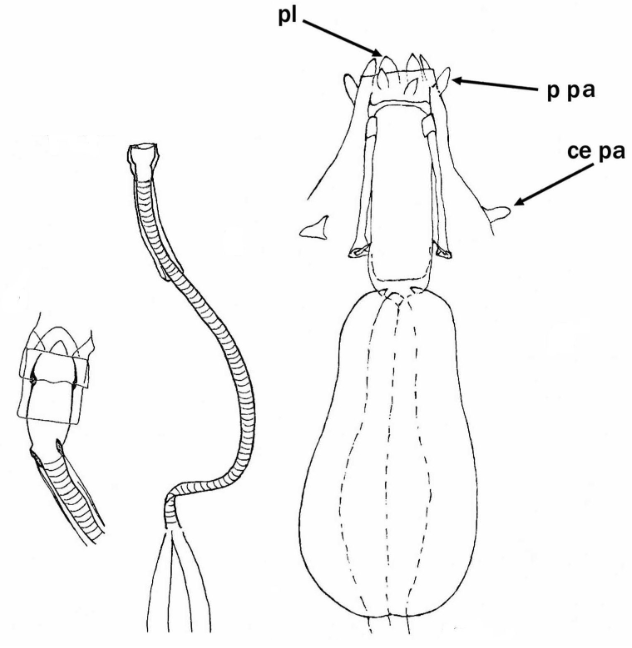
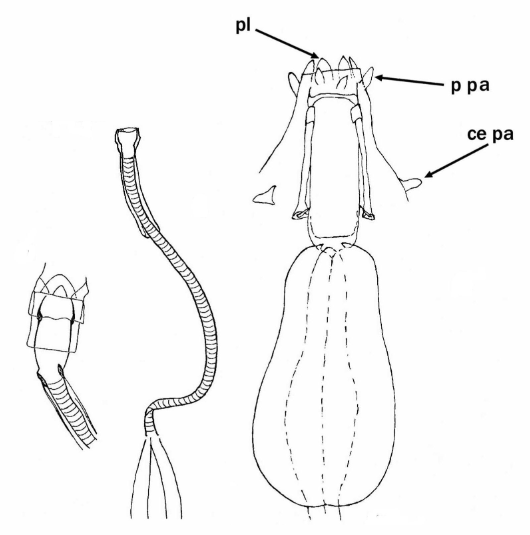
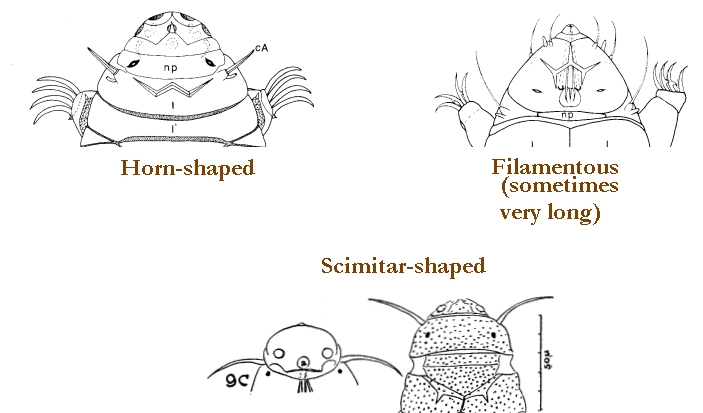
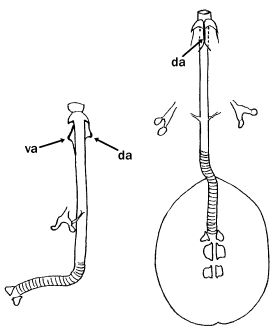
Genus description from Pilato 1987: “The bucco-pharyngeal apparatus is of the Diphascon model with the apophyses for the insertion of the muscles of the stylets in the shape of a ‘blunt hook’; the dorsal hook is different in shape and size from the ventral one with consequent asymmetry with respect to the frontal plane; the caudal processes of the apophyses for the insertion of the muscles of the stylets are pointing backwards and sideways; the furcae have the postero-lateral processes thickened at their apices.
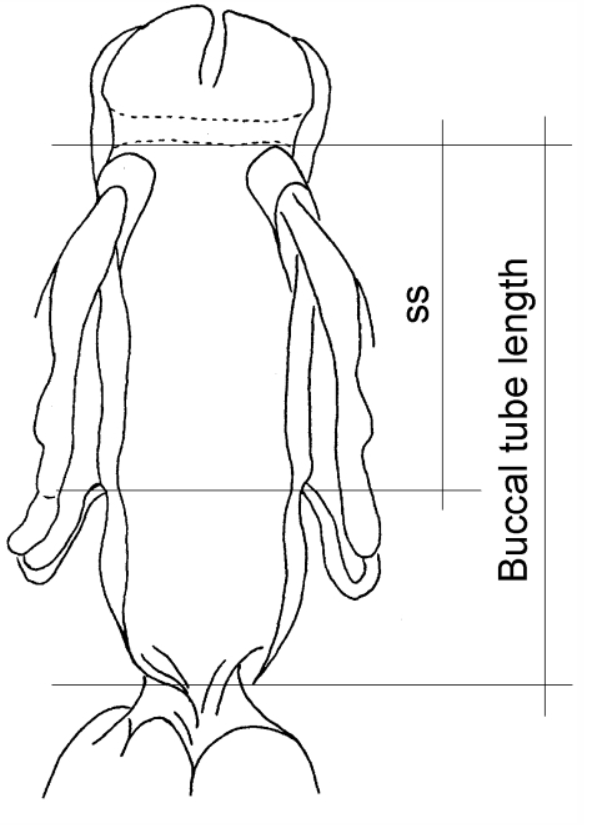
Other characters: The bucco-pharyngeal tube is narrow; the pharyngeal tube is very short, almost half as long as the pharyngeal bulb and clearly shorter than the buccal tube; the ‘drop-like’ thickening is absent; the stylet supports are inserted just after 2/3 of the buccal tube length; the pharyngeal apophyses are well developed; the pharyngeal bulb is rounded with short placoids.”
Citations:
Bertolani R, Guidetti R, Marchioro T, Altiero T, Rebecchi L, Cesari M. 2014. Phyloeny of Eutardigrada: New molecular data and their morphological support lead to the identification of new evolutionary lineages. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 76: 110-126.
Gąsiorek P, Stec D, Morek W, Michalczyk Ł. 2018. An integrative redescription of Hypsibius dujardini (Doyère, 1840), the nominal taxon for Hypsibioidea (Tardigrada: Eutardigrada). Zootaxa. 4415 (1): 45-75.
Marley NJ, McInnes SJ, Sands CJ. 2011. Phylum Tardigrada: A re-evaluation of the Parachela. Zootaxa. 2819: 51-64.
Pilato G. 1969. Schema per una nuova sistemazione delle famiglie e dei generi degli Eutardigrada. Bollettino delle Sedute della Accademia Gioenia di Scienze Naturali in Catania, Series IV. 10 (277): 181-193.
Pilato G. 1987. Revision of the genus Diphascon Plate, 1889, with remarks on the subfamily Itaquasconinae (Eutardigrada, Hypsibiidae). pp. 337-357 in Bertolani R (ed). Biology of Tardigrades: Selected symposia and monographs.